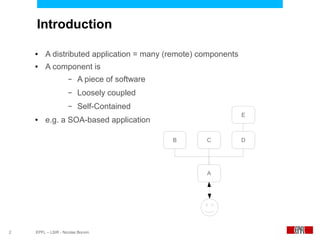
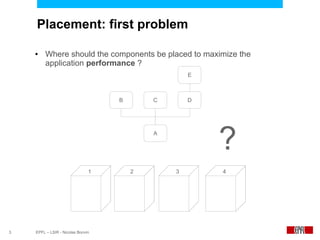
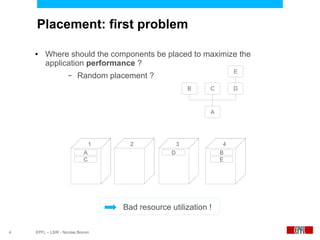
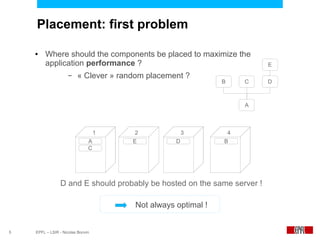
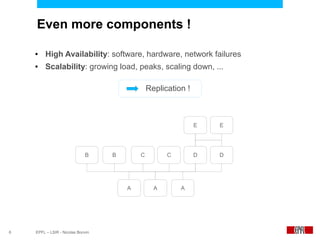
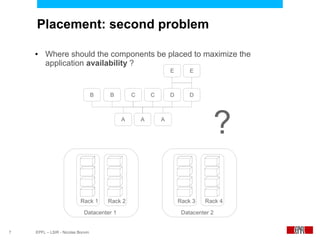
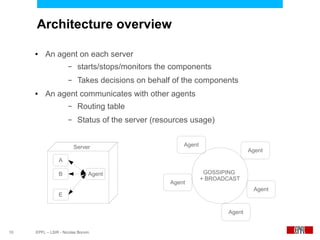
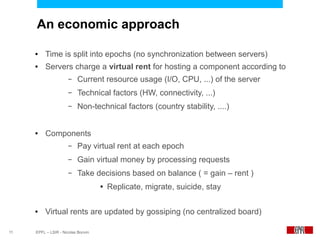
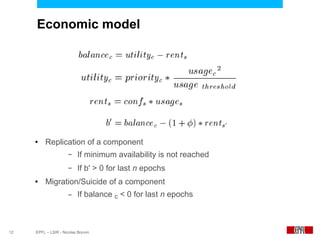
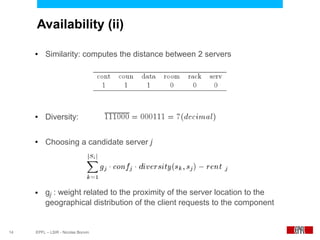
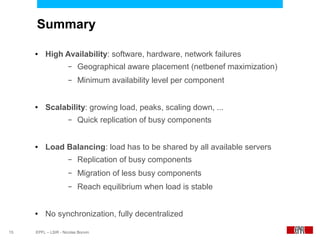
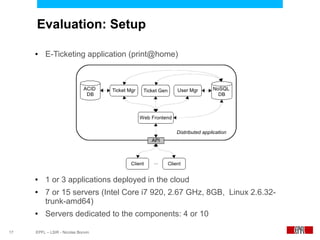
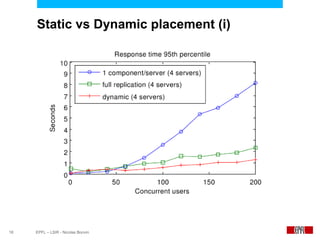
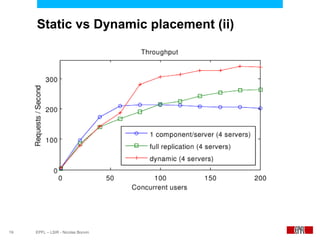
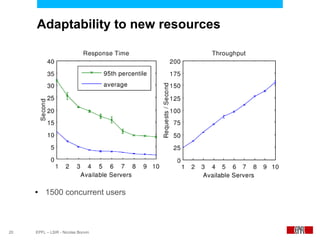
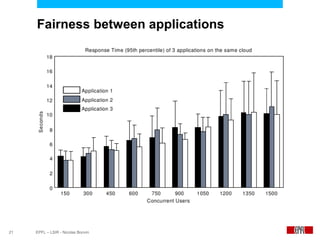
This document presents an economic approach for scalable and highly-available distributed applications called Scarce. Scarce uses an agent-based architecture where each server runs an agent that communicates with other agents to make decentralized placement decisions. Components are placed based on balancing performance, availability, and load. Components pay virtual rent to servers based on resources used, and servers charge rent. Rents are gossiped between agents with no central authority. The approach dynamically replicates, migrates, or removes components to optimize for availability and load balancing as resources and demand change over time. Evaluation shows Scarce outperforms static placement in adapting to new resources and workloads, and provides fairness between applications sharing cloud resources.