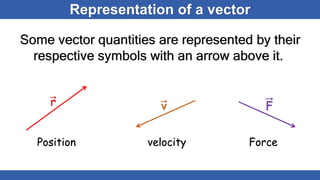
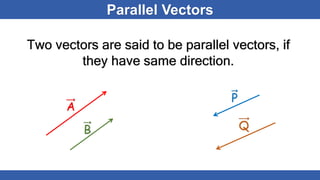
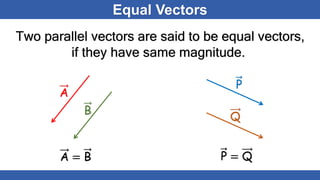
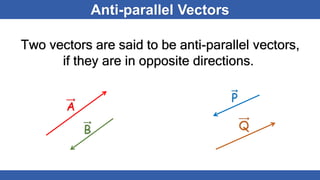
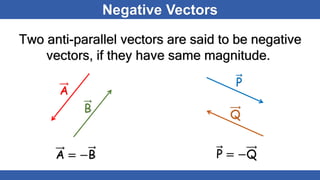
The document defines scalars and vectors. It states that a scalar is a physical quantity that only has magnitude, such as mass, length, and temperature. A vector is a physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction, such as position, displacement, velocity, and force. The document discusses different types of vectors based on their orientation, such as parallel, anti-parallel, and collinear vectors. It also covers vector addition and properties like commutativity and associativity.