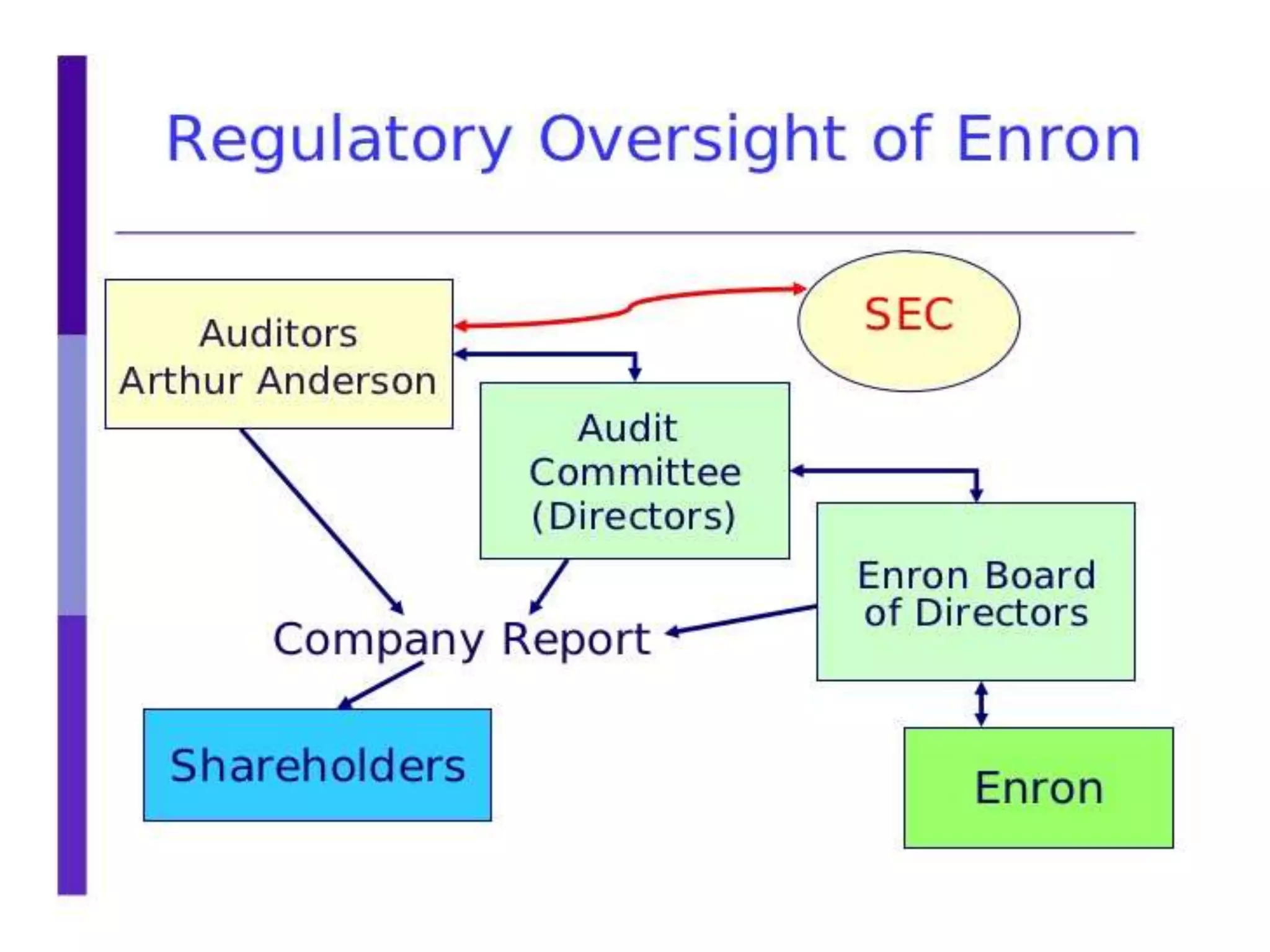
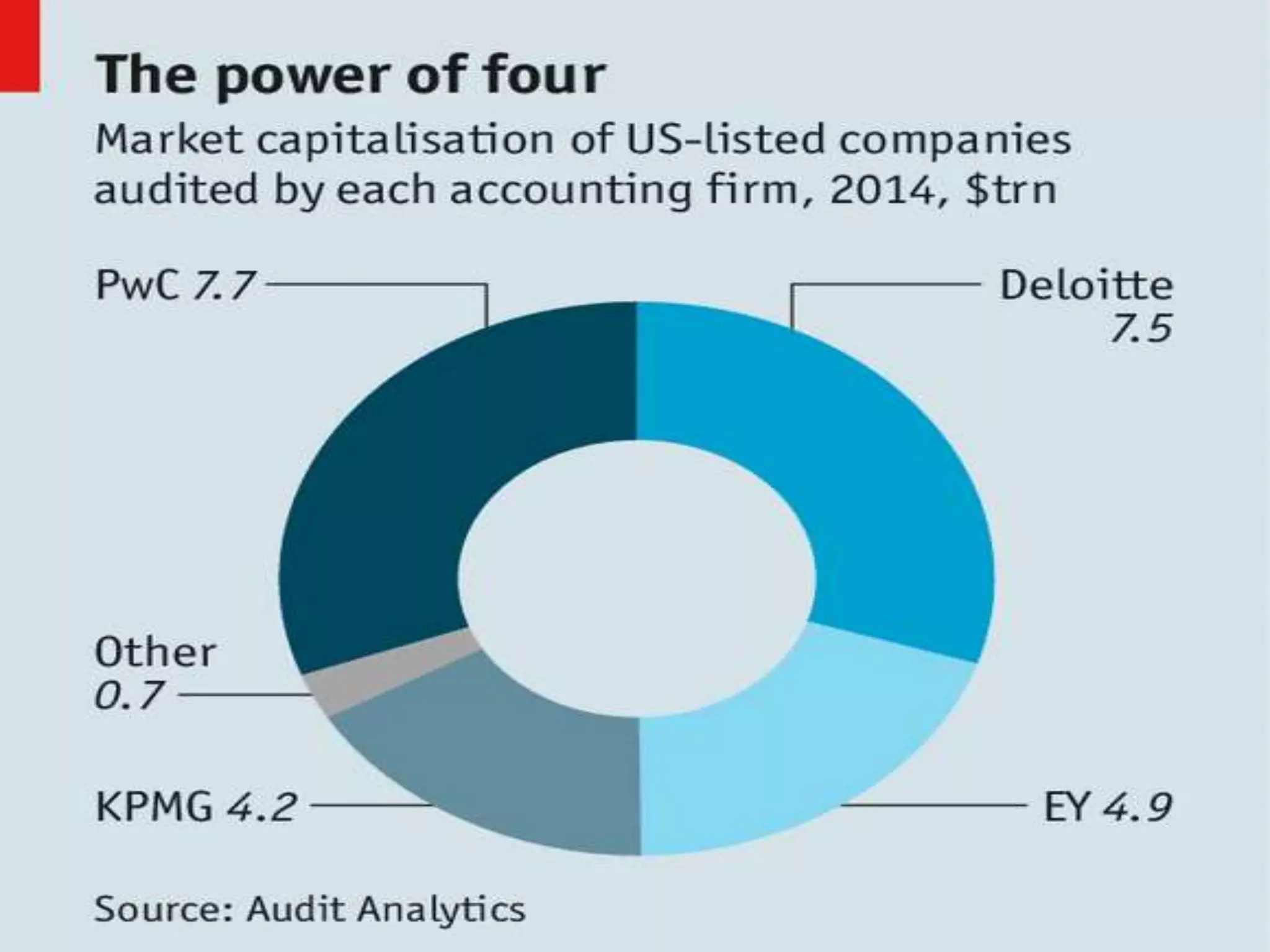
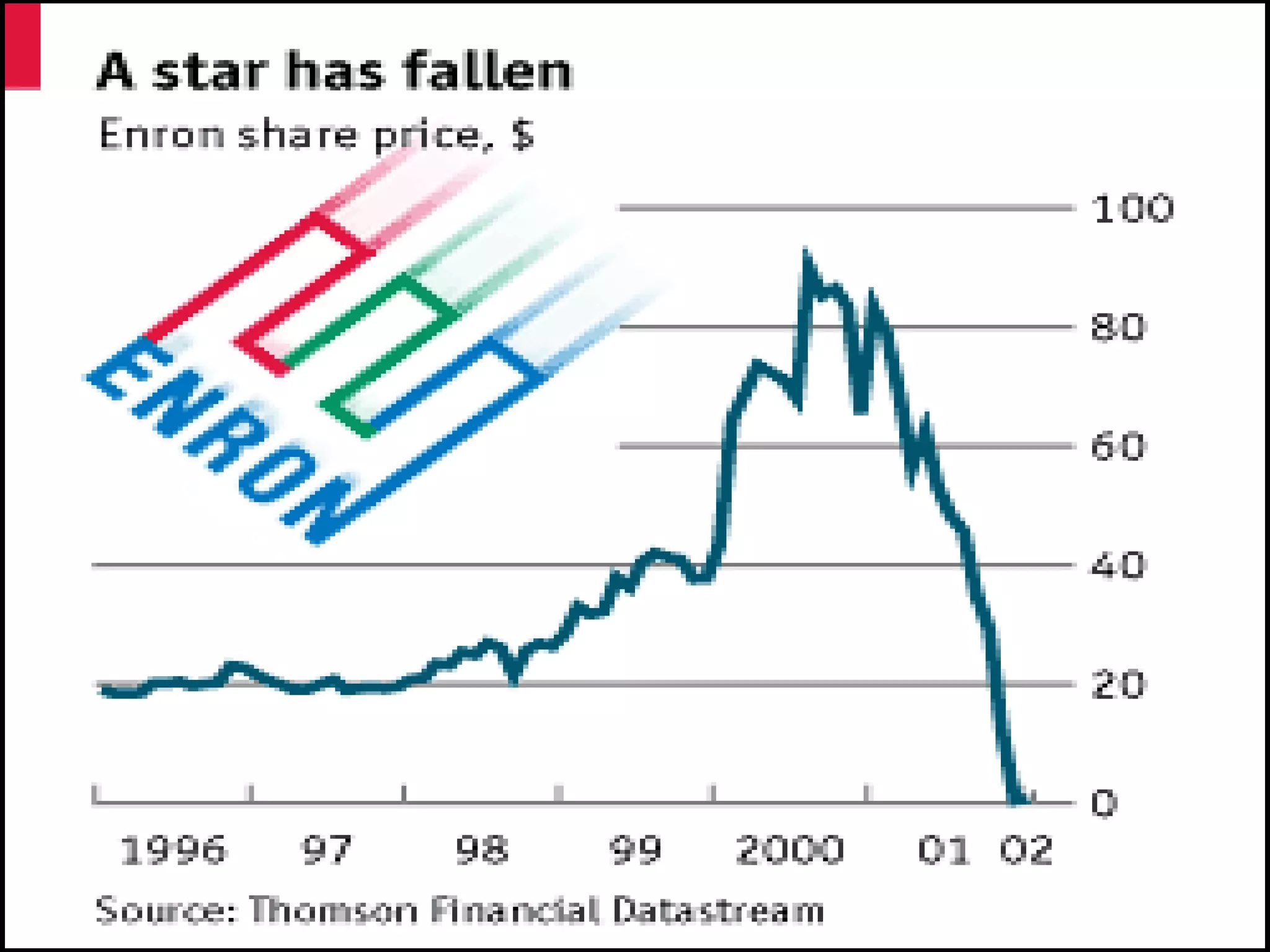
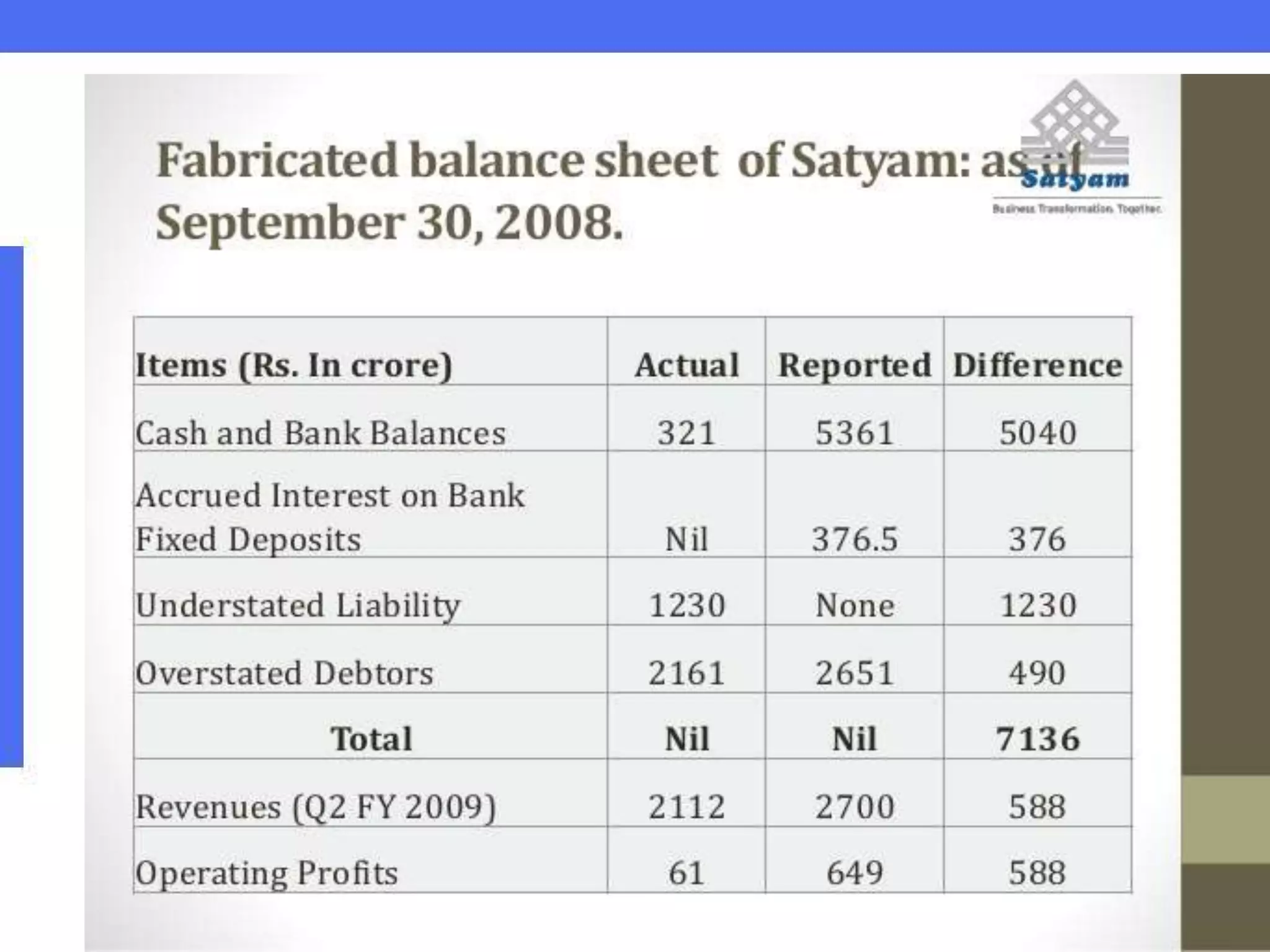
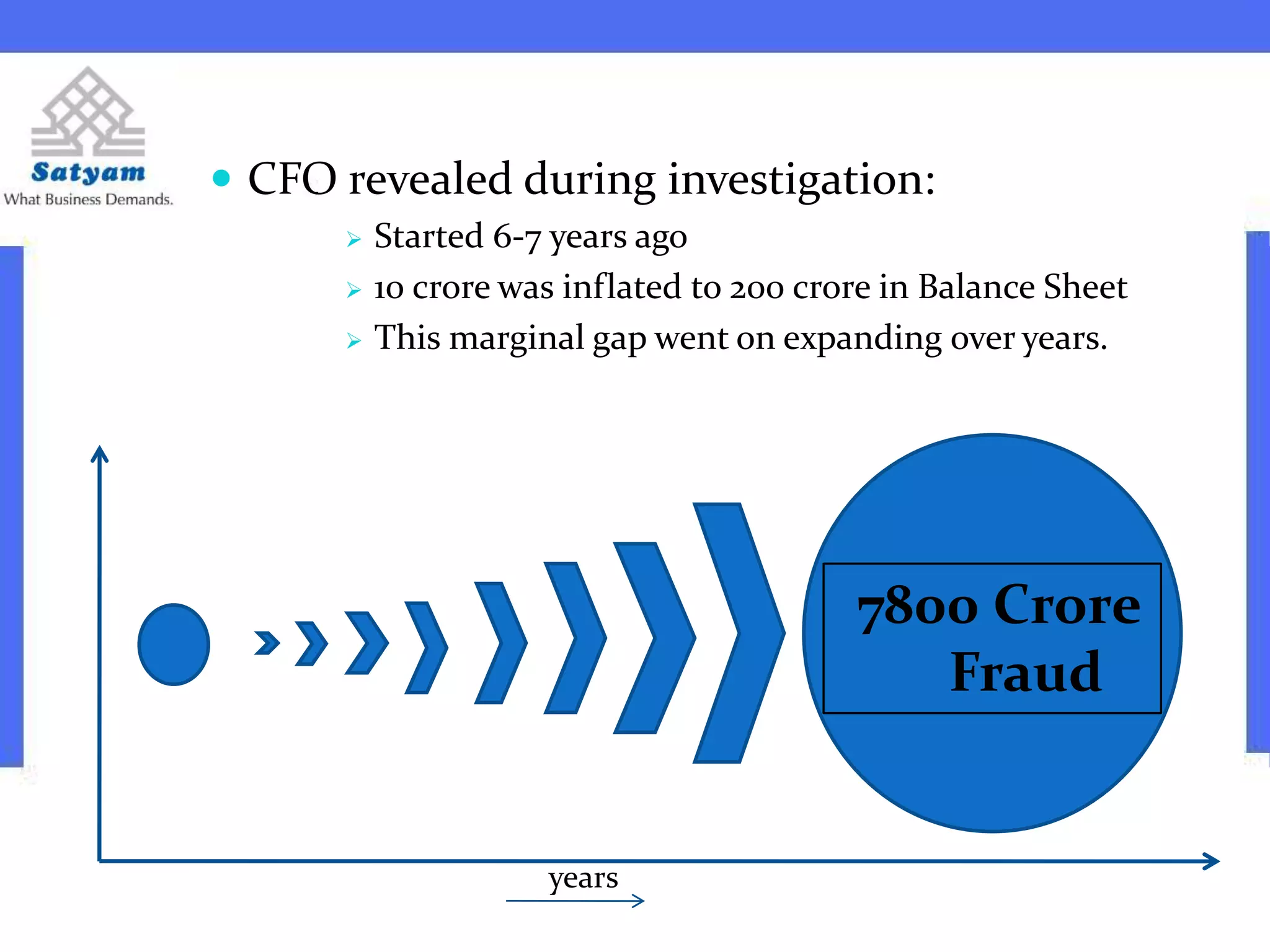
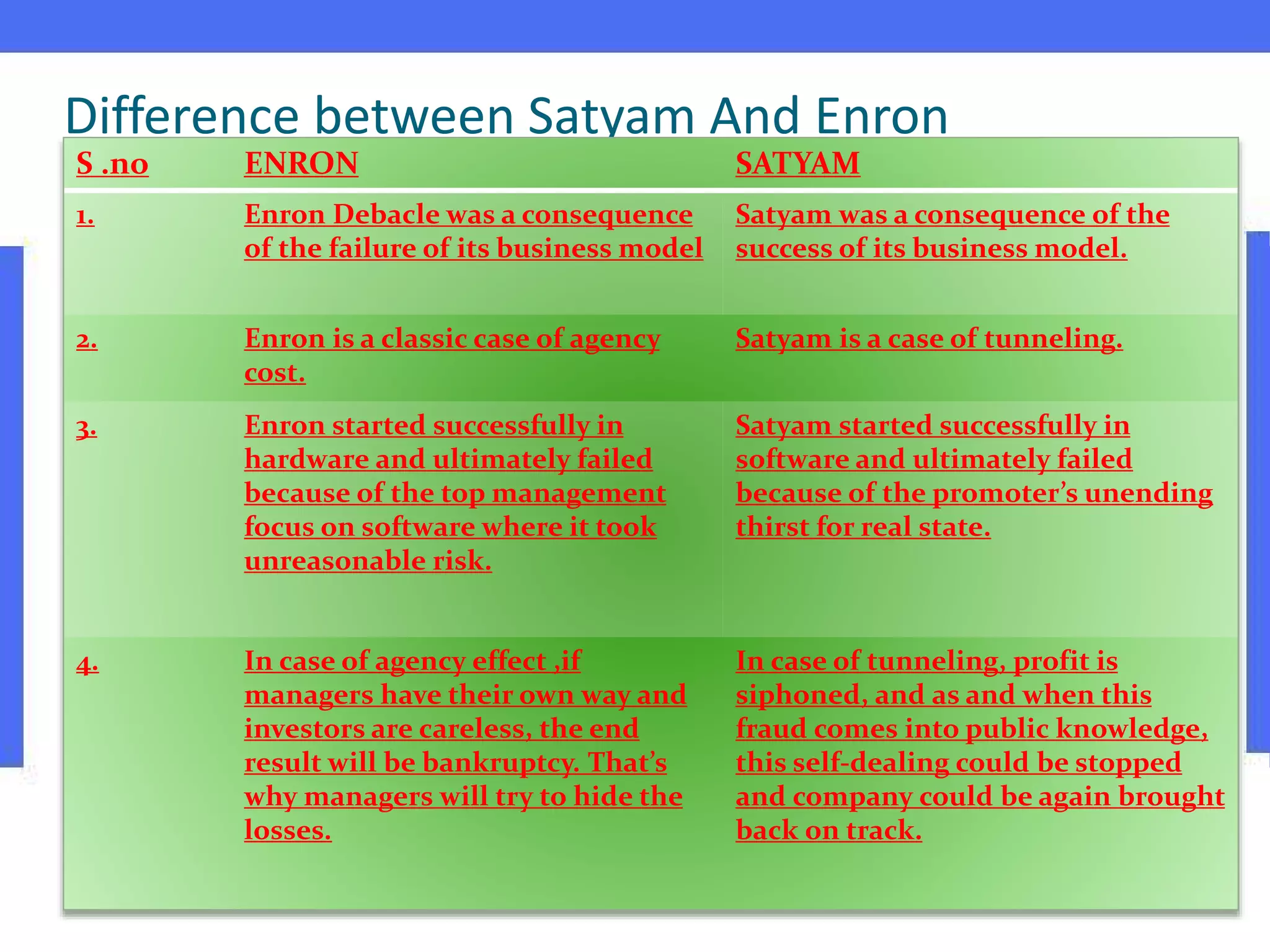
Ramalinga Raju founded Satyam Computers in 1987 and was its chairman until 2009 when he resigned after admitting to a corporate accounting fraud of over 7,800 crores. He had been inflating profits and fudging accounts for the past 7 years in an attempt to fill growing gaps in Satyam's financials and avoid hostile takeovers. When all attempts to cover the fraud failed, Raju confessed in a letter, sending shockwaves through India's markets and corporate world. An investigation into Satyam uncovered the roles of other senior executives in the massive accounting scandal.