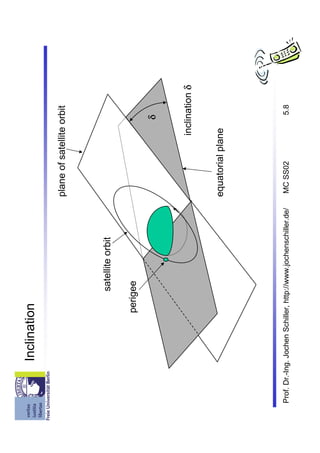
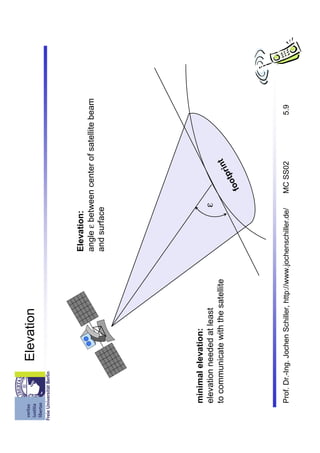
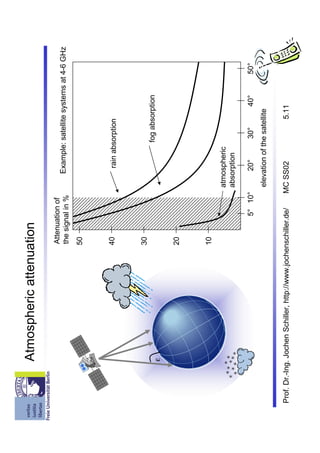
The document discusses satellite communication systems. It provides a brief history of satellite communication starting in 1945. It describes some of the basic concepts including orbital mechanics, inclination, elevation, and link budgets. It also discusses different types of satellite orbits including LEO, MEO, GEO and HEO orbits. Classical satellite systems are also summarized, focusing on components like the gateway, mobile user link, and intersatellite link. Key applications of satellite systems are mentioned such as weather satellites, broadcast satellites, navigation satellites, and extending cellular networks.





![Satellite period and orbits
24 satellite
velocity [ x1000 km/h] period [h]
20
16
12
8
4
synchronous distance
35,786 km
10 20 30 40 x106 m
radius
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 5.6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c05-satellitesystems-121225165238-phpapp02/85/satellite-systems-6-320.jpg)










![Overview of LEO/MEO systems
Iridium Globalstar ICO Teledesic
# satellites 66 + 6 48 + 4 10 + 2 288
altitude 780 1414 10390 ca. 700
(km)
coverage global ±70° latitude global global
min. 8° 20° 20° 40°
elevation
frequencies 1.6 MS 1.6 MS ↑ 2 MS ↑ 19 ↓
[GHz 29.2 ↑ 2.5 MS ↓ 2.2 MS ↓ 28.8 ↑
(circa)] 19.5 ↓ 5.1 ↑ 5.2 ↑ 62 ISL
23.3 ISL 6.9 ↓ 7↓
access FDMA/TDMA CDMA FDMA/TDMA FDMA/TDMA
method
ISL yes no no yes
bit rate 2.4 kbit/s 9.6 kbit/s 4.8 kbit/s 64 Mbit/s ↓
2/64 Mbit/s ↑
# channels 4000 2700 4500 2500
Lifetime 5-8 7.5 12 10
[years]
cost 4.4 B$ 2.9 B$ 4.5 B$ 9 B$
estimation
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 5.20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c05-satellitesystems-121225165238-phpapp02/85/satellite-systems-20-320.jpg)