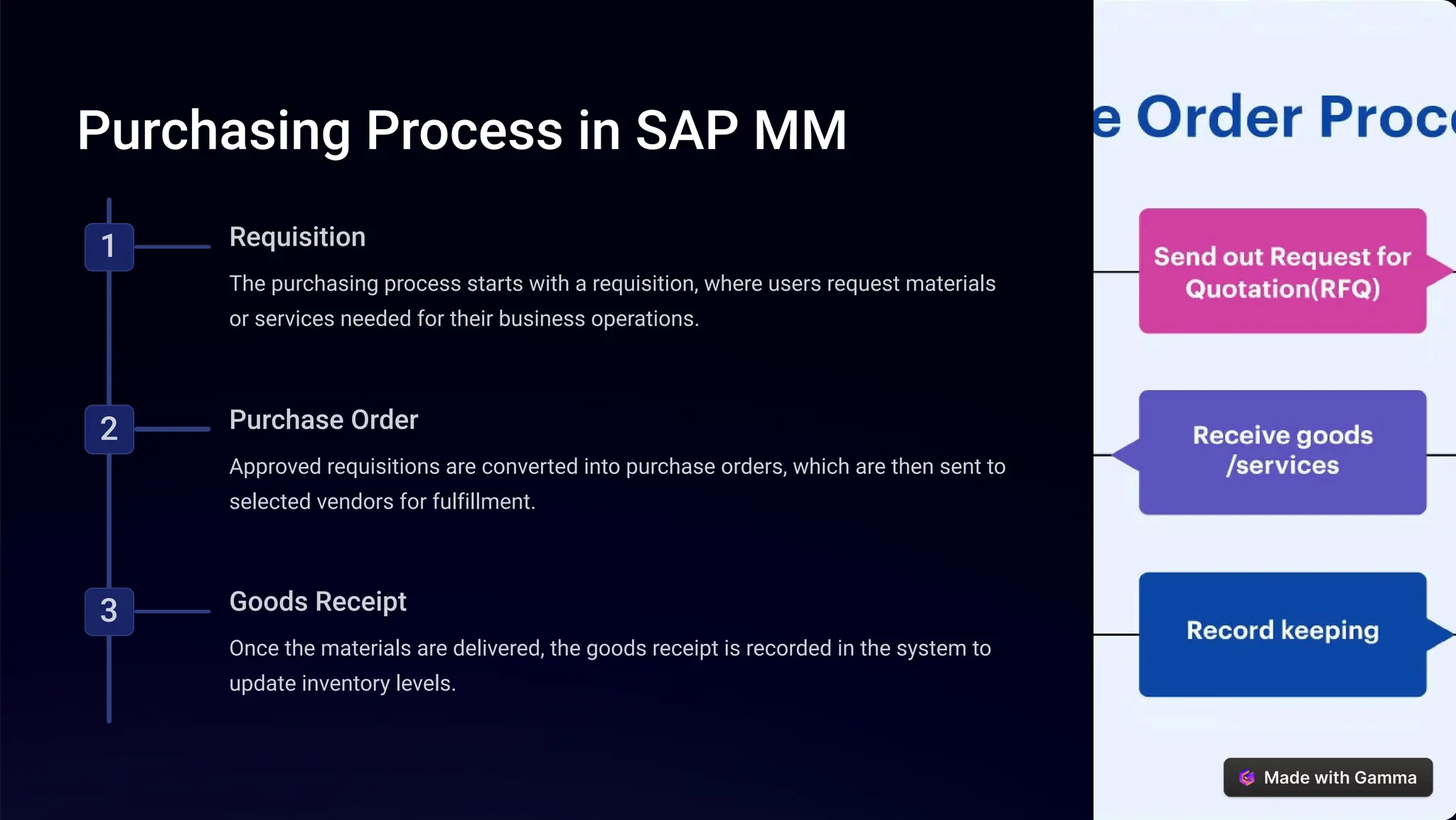
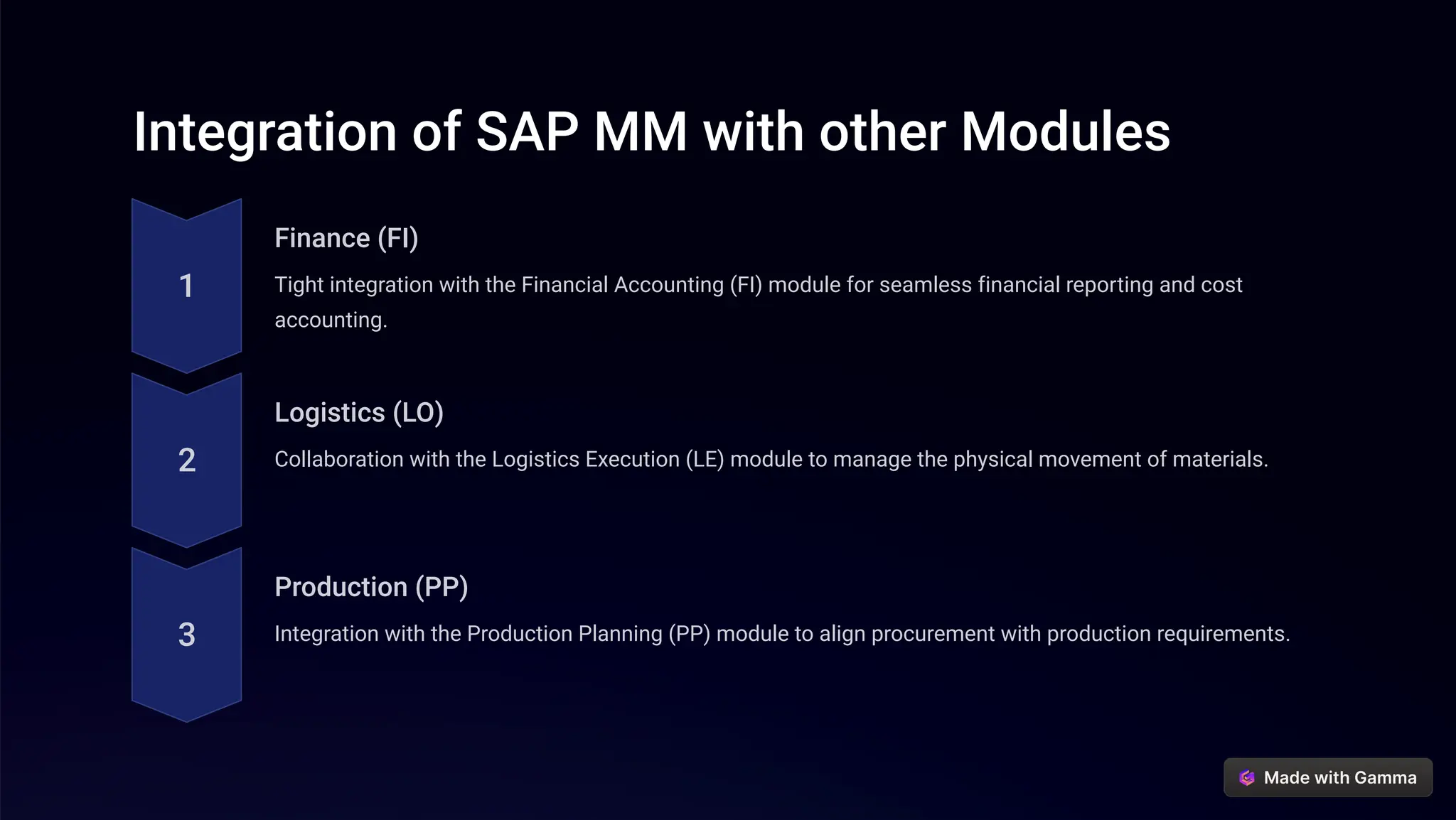
The SAP Materials Management (MM) module is designed to manage procurement, inventory, and vendor relationships, optimizing supply chain processes. It encompasses functions such as requisitioning, purchase orders, inventory control, vendor management, and integration with other SAP modules such as finance and production. The document also outlines best practices for process automation, data governance, and continuous improvement in utilizing SAP MM.