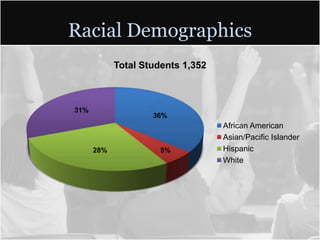
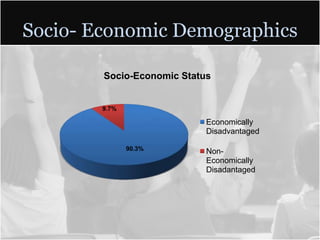
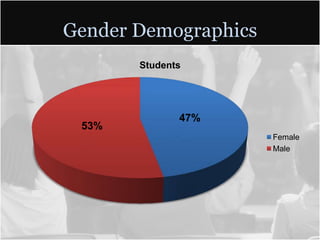
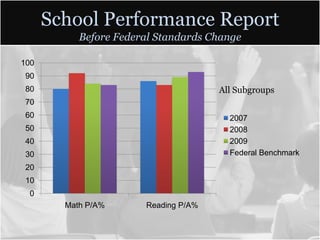
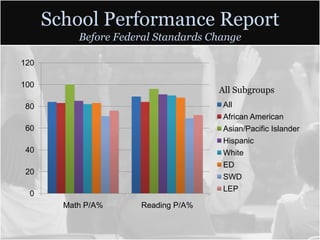
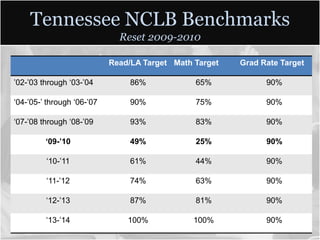
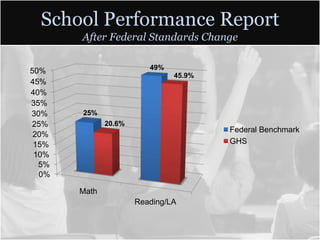
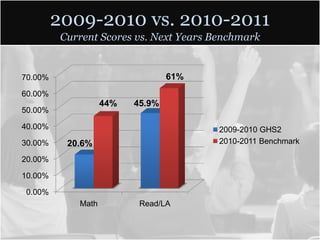
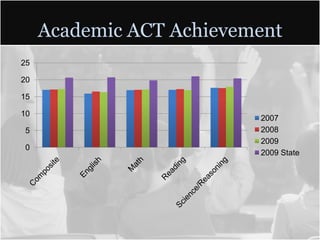
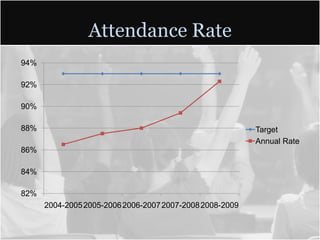
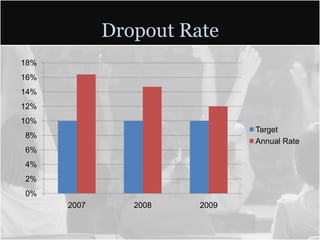
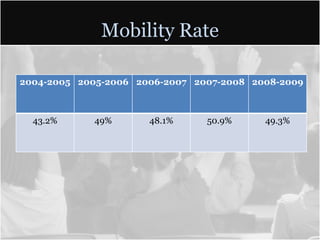
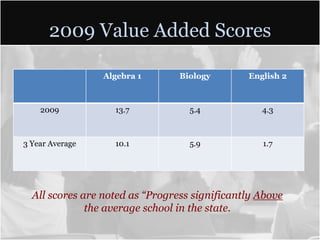
This document summarizes data from Glencliff High School in Tennessee from 2010. It shows that the school has highly diverse student body from 44 countries speaking 40 languages. It also shows improvements in freshman promotion rates since implementing a Freshman Academy. Additional data outlines the school's performance, demographics, attendance, mobility, and Adequate Yearly Progress history. Scores on state standardized tests and ACT exams are provided. Throughout, the importance of recognizing the individual students behind the data is emphasized.