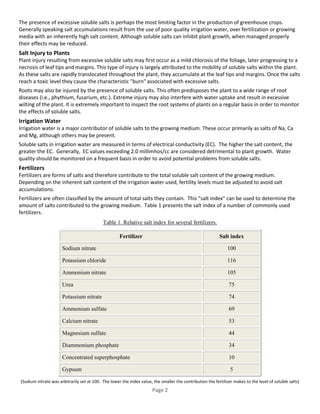
Granular fertilizers can cause higher salt concentrations in soil solutions compared to liquid fertilizers due to requiring more water to dissolve. High salt concentrations can decrease seed germination or damage seedlings. The salt index expresses the increase in osmotic pressure of a fertilizer solution relative to sodium nitrate, with higher analysis fertilizers having a lower salt index. Excessive soluble salts from sources like poor irrigation water, over-fertilization, or high salt growing media can inhibit plant growth and cause leaf tip burn or root damage. Managing salt levels involves using well-draining media, leaching salts, adjusting fertilizer and irrigation based on water quality, and maintaining adequate moisture.