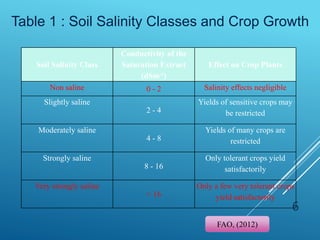
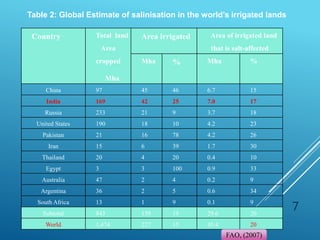
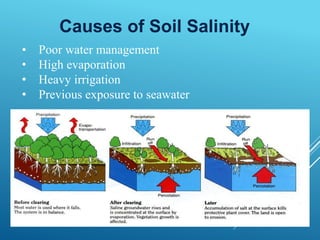
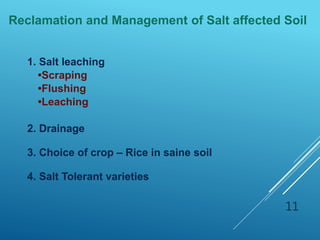
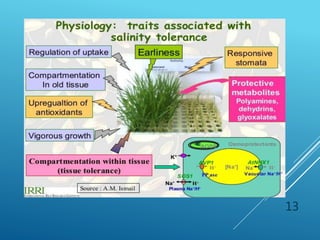
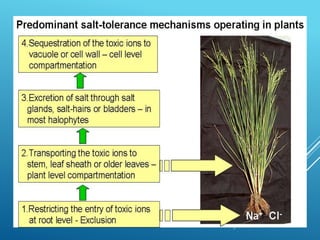
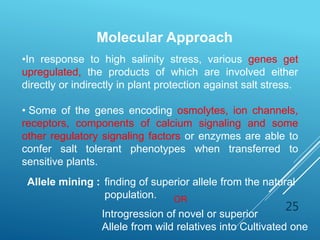
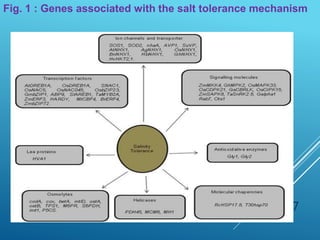
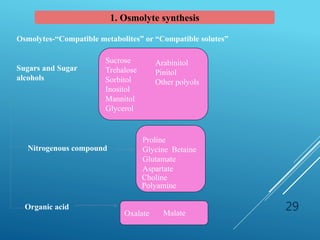
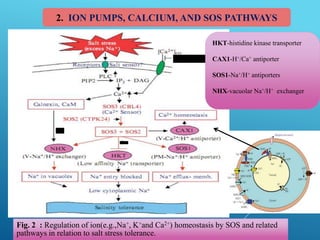
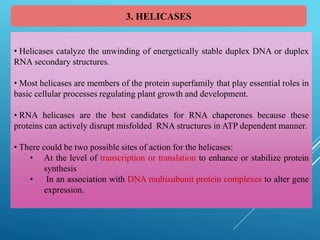
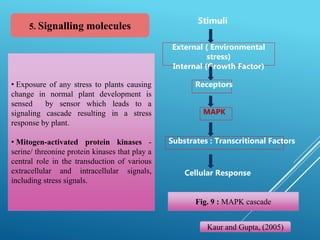
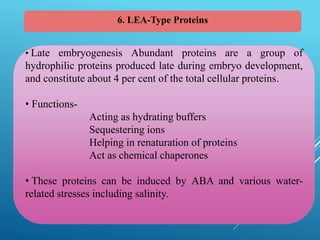
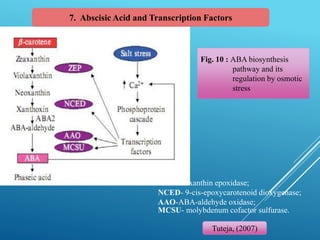
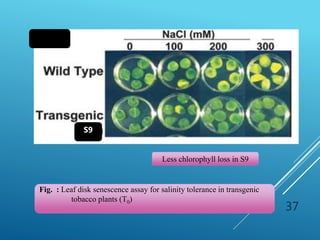
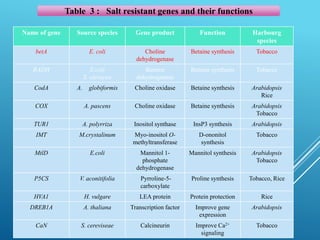
This document discusses breeding for salinity tolerance in crops. It notes that salinity is a major factor limiting crop productivity, affecting 6% of the world's land and 20% of irrigated areas. Salinity reduces water availability to plants and can cause ion toxicity. The document outlines various mechanisms of salt tolerance in plants, including osmolyte synthesis, ion pumps and transporters, reactive oxygen species management, and signaling pathways. It discusses conventional breeding approaches and their limitations, as well as modern non-conventional approaches like molecular breeding and transgenics. Overall, the document provides an overview of the challenges of soil salinity for agriculture and different strategies for developing salt-tolerant crop varieties.