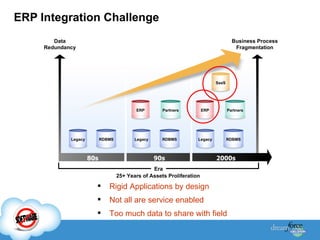
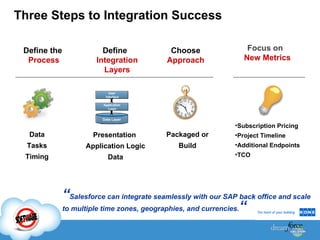
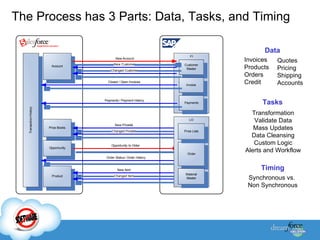
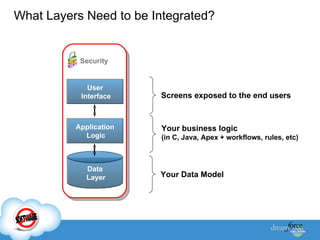
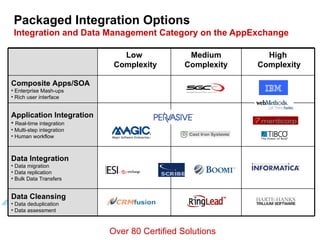
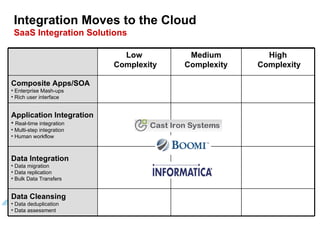
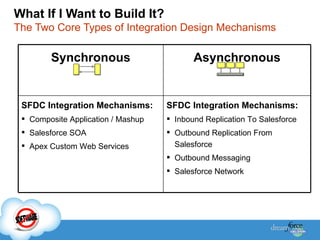
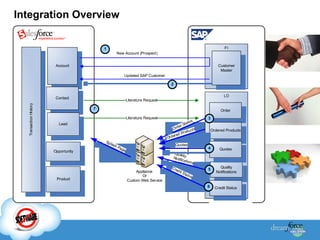
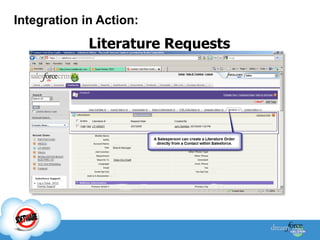
The document discusses best practices for integrating ERP data with Salesforce. It outlines three steps for integration success: focus on new metrics, define integration processes, and choose an integration approach. Common integration layers are data, application logic, and user interface. Packaged integration options on the AppExchange include data integration and application integration solutions. Custom built integrations can use synchronous or asynchronous design. The document also provides an example integration project between Brady Corporation's SAP system and Salesforce to enable 360-degree customer views, automate manual processes, and reduce costs.