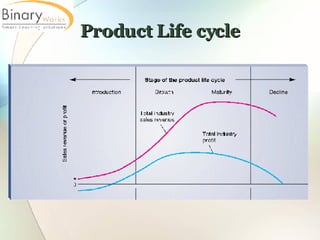
The document discusses various topics related to managing products and services over their lifecycles, including:
1) Common reasons products may resist change or fail include cultural/image barriers, psychological barriers, risk barriers, lack of incentive to change, incompatibility with habits, and lack of usage barriers.
2) When managing a product's lifecycle, companies can modify the product, modify the market, or reposition the product. Products may be repositioned in reaction to competitors, catching trends, or reaching new markets.
3) Key considerations for new services include inseparability from provider, variability in quality, intangibility, and different levels of customer assessment pre- and post- purchase.