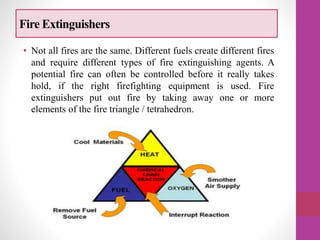
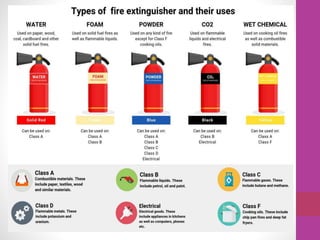
Fire safety in laboratories is important. Different types of fire extinguishers are designed for different classes of fires. It is important to know which type of extinguisher to use for various fires. All laboratories should have fire extinguishers located inside or directly outside, and they should be inspected annually. Personnel should be trained on how to use the extinguishers and the evacuation plan. In case of a fire alarm, all personnel must stop work, leave belongings, and calmly evacuate to the parking area. The PASS method can help remember how to use an extinguisher - Pull the pin, Aim at the base of the fire, Squeeze the handle, Sweep side to side until the fire is out