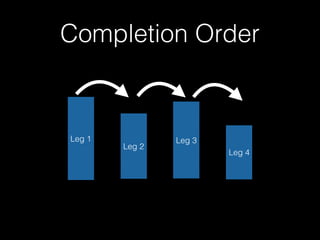
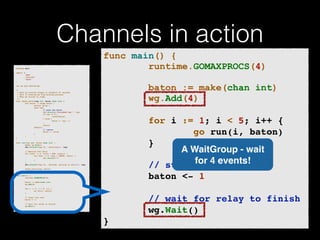
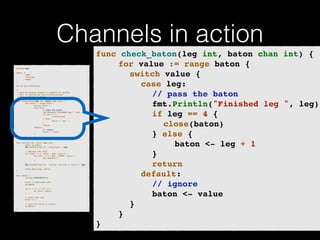
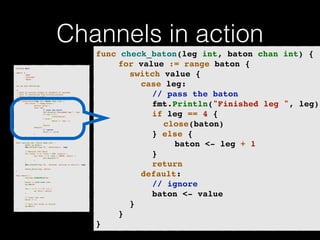
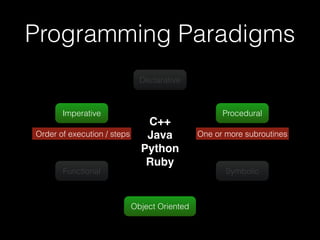
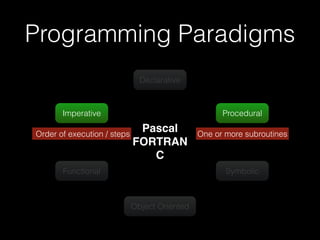
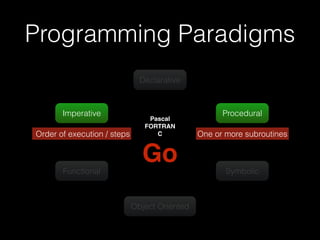
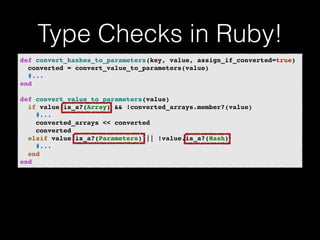
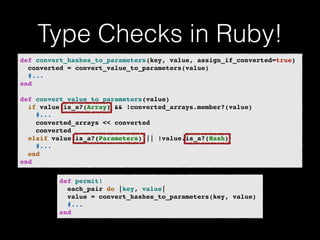
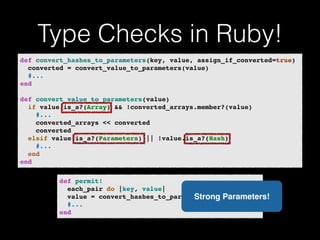
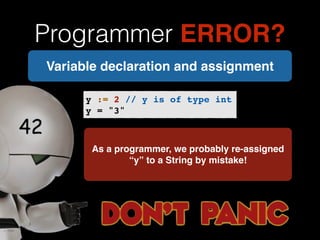
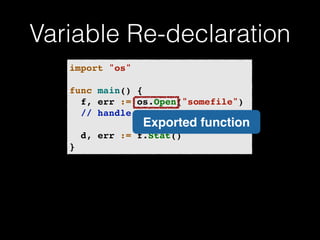
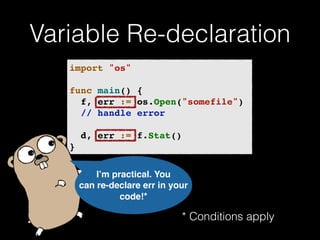
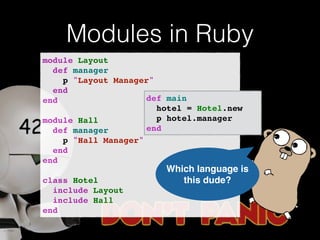
The document discusses the Go programming language and how it differs from Ruby. It provides examples of Go code demonstrating type declarations, embedded types, exported variables and functions, and variable redeclaration. It also discusses some concepts in Go like interfaces, channels, and concurrency that are different from Ruby. The document suggests that Go teaches programmers awareness about variables, types, and errors that can improve Ruby code.
























































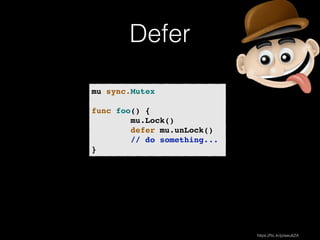
![Lets Go a little more!
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Dimensions)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}
Type Declaration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-73-320.jpg)
![Lets Go a little more!
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Dimensions)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}
Exported Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-74-320.jpg)
![Lets Go a little more!
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Dimensions)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}
Exported Array
The size in Array is part of the type!
[2]float32 != [3]float32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-75-320.jpg)
![Lets Go a little more!
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Dimensions)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}
Embedding!
(Not inheritance)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-76-320.jpg)
![Lets Go a little more!
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Dimensions)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}
hotel.Dimensions and not
hotel.Hall.Dimensions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-77-320.jpg)
![Lets Go a little more!
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Name)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
Dimensions)!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-78-320.jpg)
![Lets Go a little more!
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Name)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-79-320.jpg)
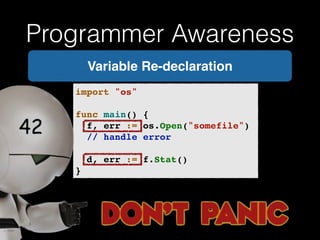
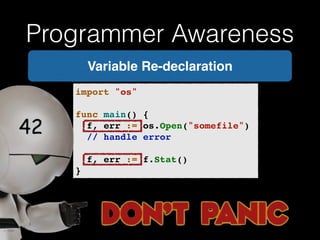
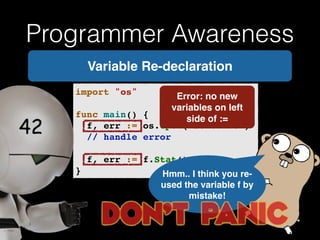
![Programmer Awareness
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Name)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-80-320.jpg)
![Programmer Awareness
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Name)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}
Which Name should
I use?
Error: Ambiguous
selector hotel.Name!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-81-320.jpg)
![Programmer Awareness
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Name)Hall.!
Name)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-82-320.jpg)
![Programmer Awareness
type Layout struct {!
! Name string!
Capacity int!
}!
!
type Hall struct {!
! Name string!
! Dimensions [2]float32!
}!
!
type Hotel struct {!
! Location string!
! Hall!
! Layout!
}
func main() {!
! hotel := Hotel{}!
! fmt.Println(hotel.Hall.Name)!
!
! h := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
! for name, _ := range h {!
! ! fmt.Println(name)!
! }!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-83-320.jpg)

![Programmer Awareness
Iterating a Hash
hotels := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
for name, _ := range hotels {!
! fmt.Println(name)!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-87-320.jpg)
![Programmer Awareness
Iterating a Hash
hotels := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
for name, _ := range hotels {!
! fmt.Println(name)!
}
Map of strings and Hotels](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-88-320.jpg)
![Programmer Awareness
Iterating a Hash
hotels := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
for name, _ := range hotels {!
! fmt.Println(name)!
}
Easy iteration syntax!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-89-320.jpg)
![Programmer Awareness
Iterating a Hash
hotels := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
for name, _ := range hotels {!
! fmt.Println(name)!
} Blank Identifier - ignore value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-90-320.jpg)
![Programmer Awareness
Iterating a Hash
hotels := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
for name, _ := range hotels {!
! fmt.Println(name)!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-91-320.jpg)
![Programmer Awareness
Iterating a Hash
hotels := make(map[string]Hotel)!
!
for name, _ := range hotels {!
! fmt.Println(name)!
}
Bad practice! !
I’ll randomise the
order!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyrubymustgo-141013124844-conversion-gate02/85/RubyConf-Portugal-2014-Why-ruby-must-go-92-320.jpg)