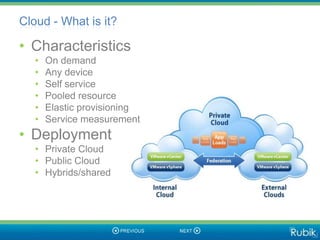
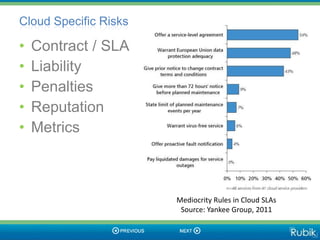
The document discusses the risks and benefits of cloud computing. It describes different types of cloud services including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Some key risks discussed include security, service interruptions, privacy, and outsourcing risks related to intellectual property and data ownership. However, the document also notes that cloud computing provides benefits like flexibility, scalability, cost savings, and increased security compared to traditional IT systems. It argues that while risks exist, they can be mitigated, and cloud adoption is important for competitiveness.