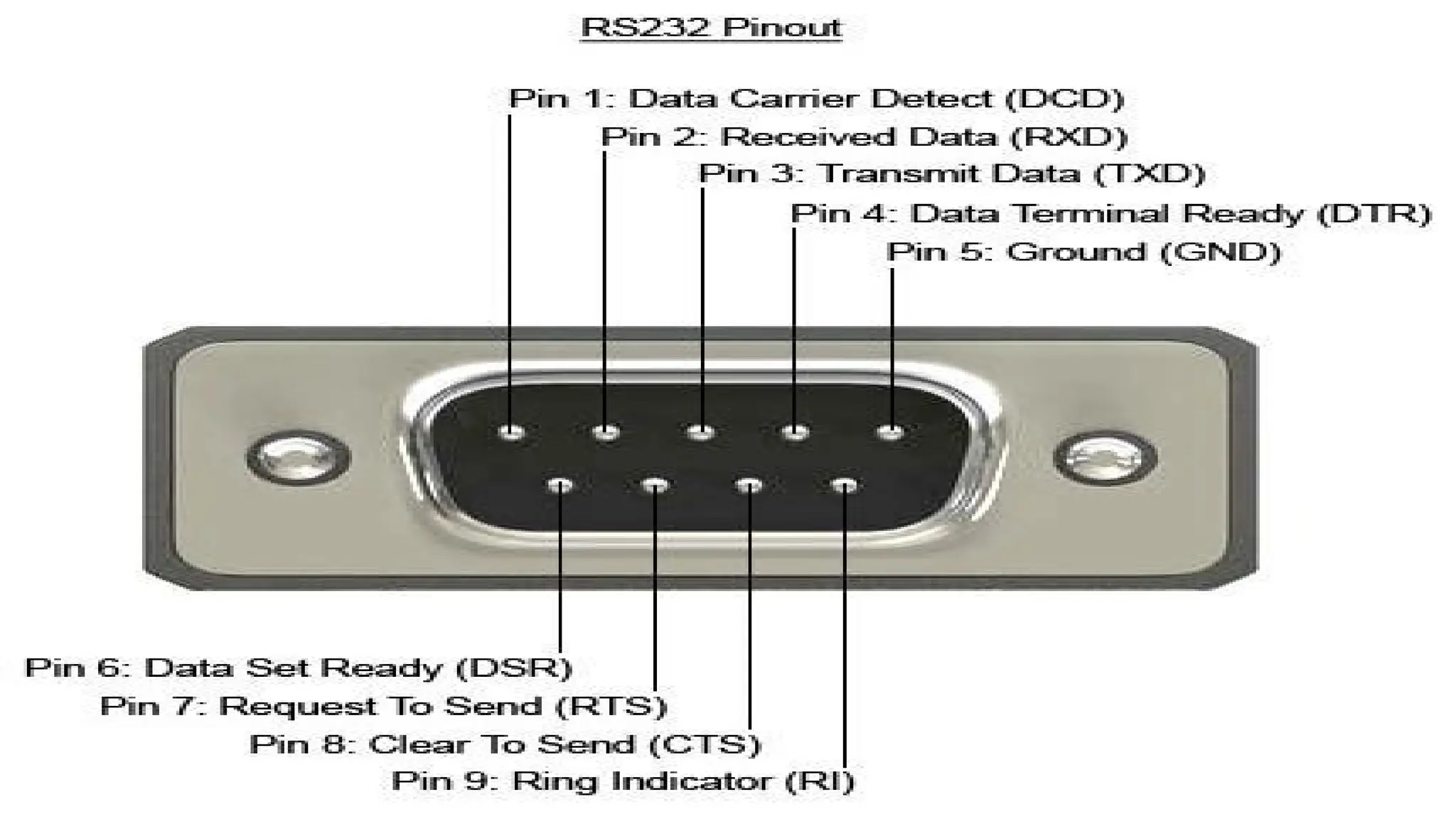
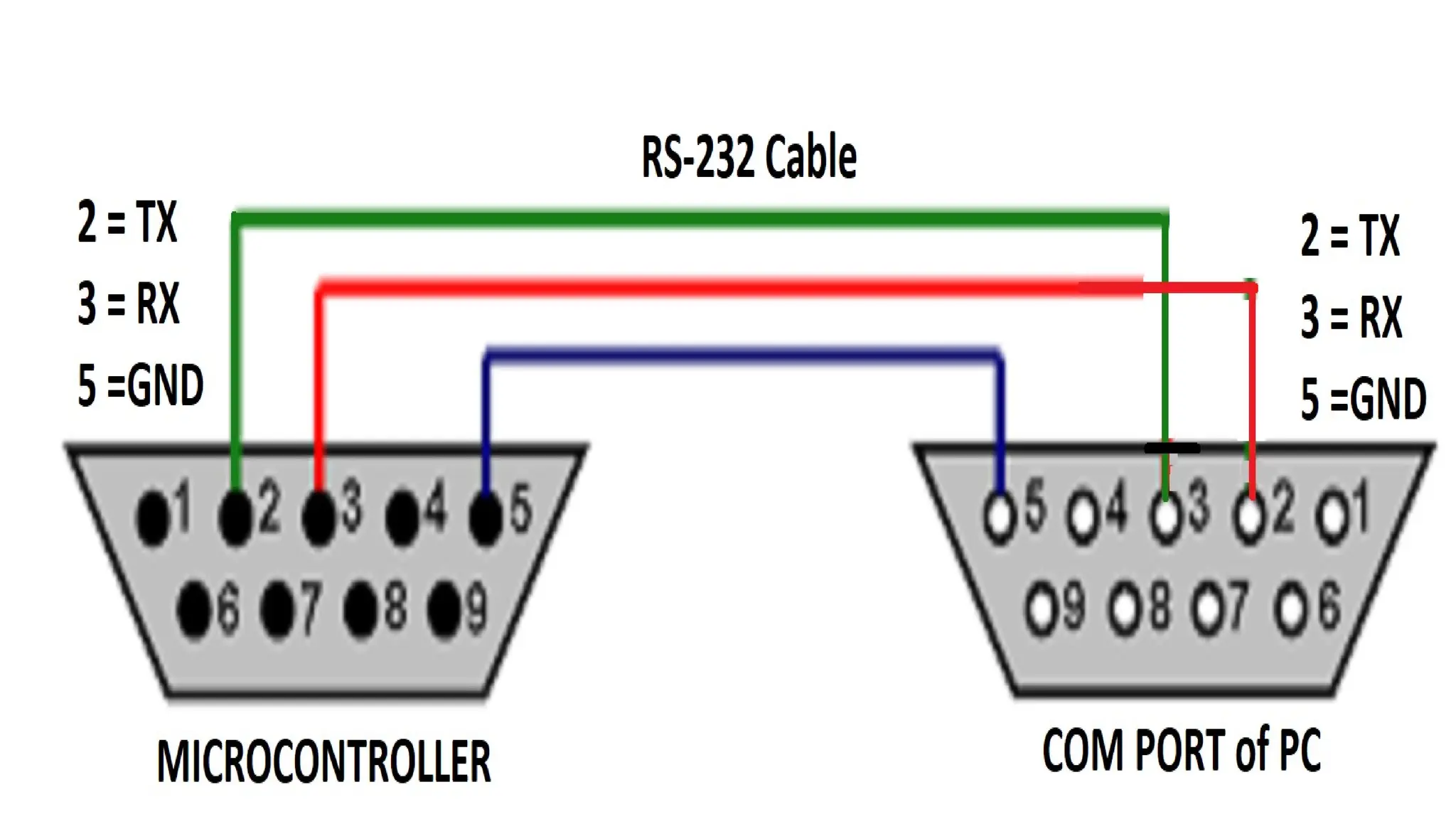
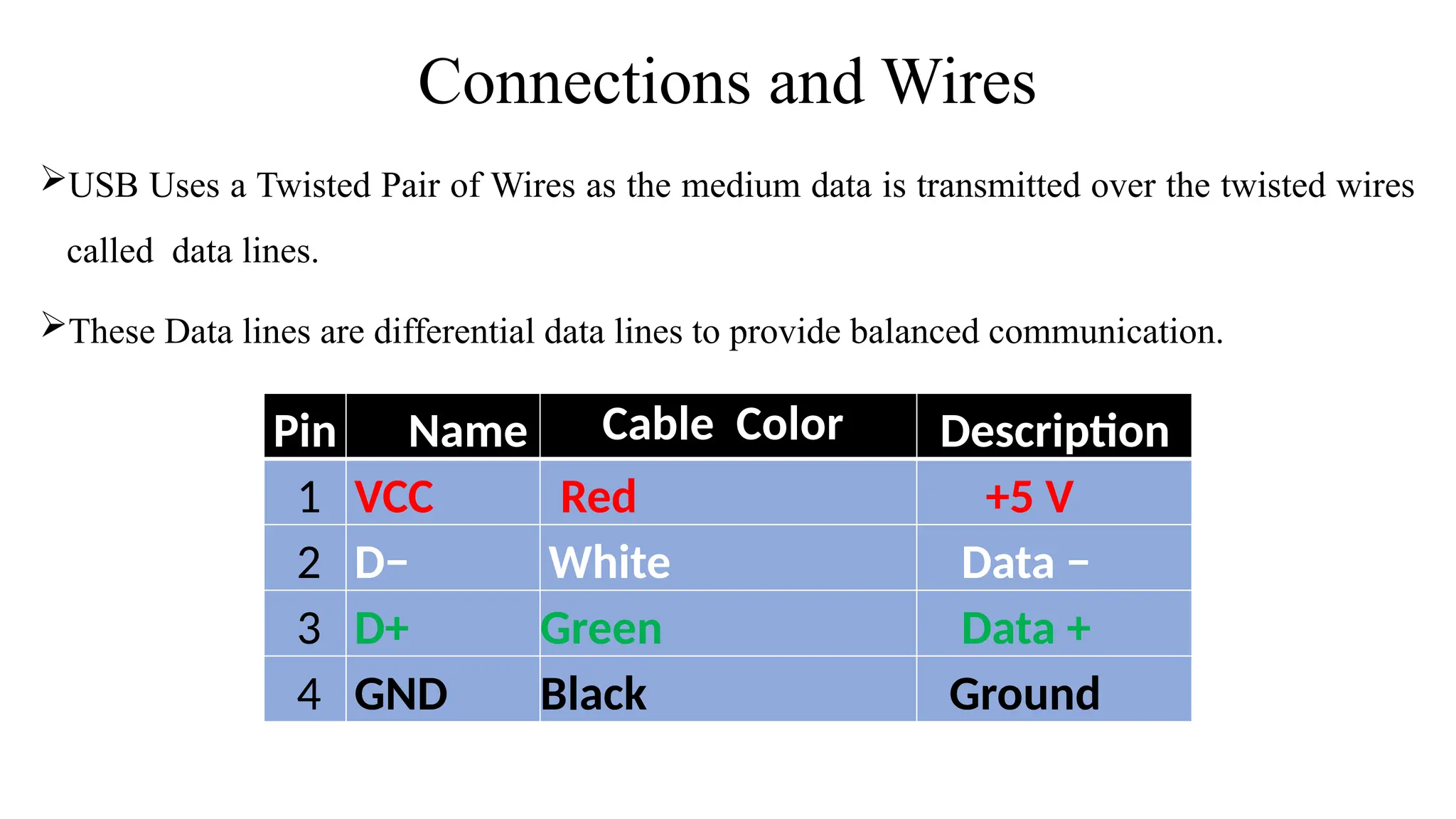
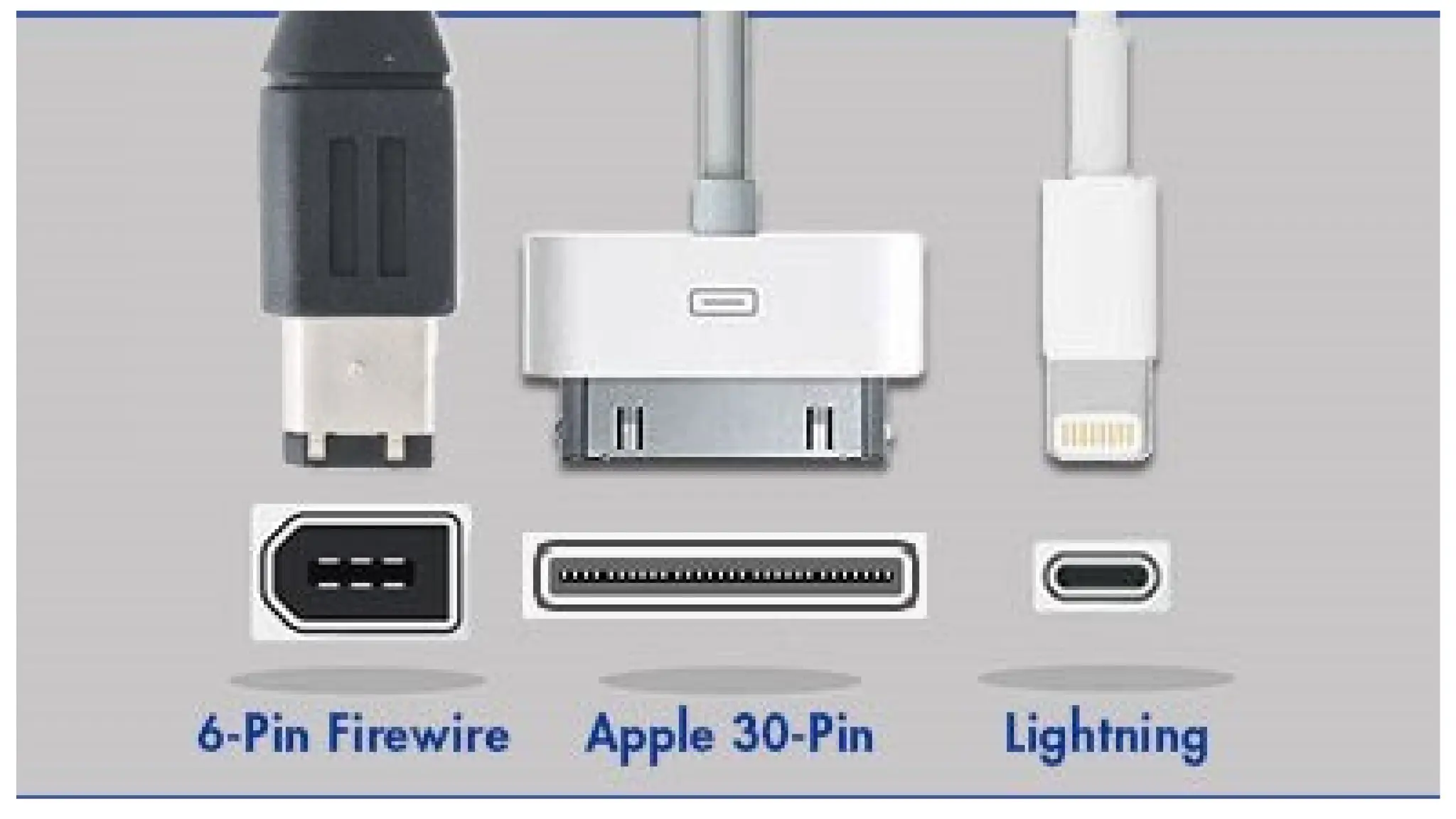
The document explains handshaking in data communication, detailing hardware and software methods for flow control. It provides an overview of USB, including its history, key features, and different connector types, while highlighting the evolution from USB 1.0 to USB 3.2 and beyond. Additionally, it outlines various developments in connector technology, including Apple's Lightning connector and MHL (Mobile High-Definition Link).