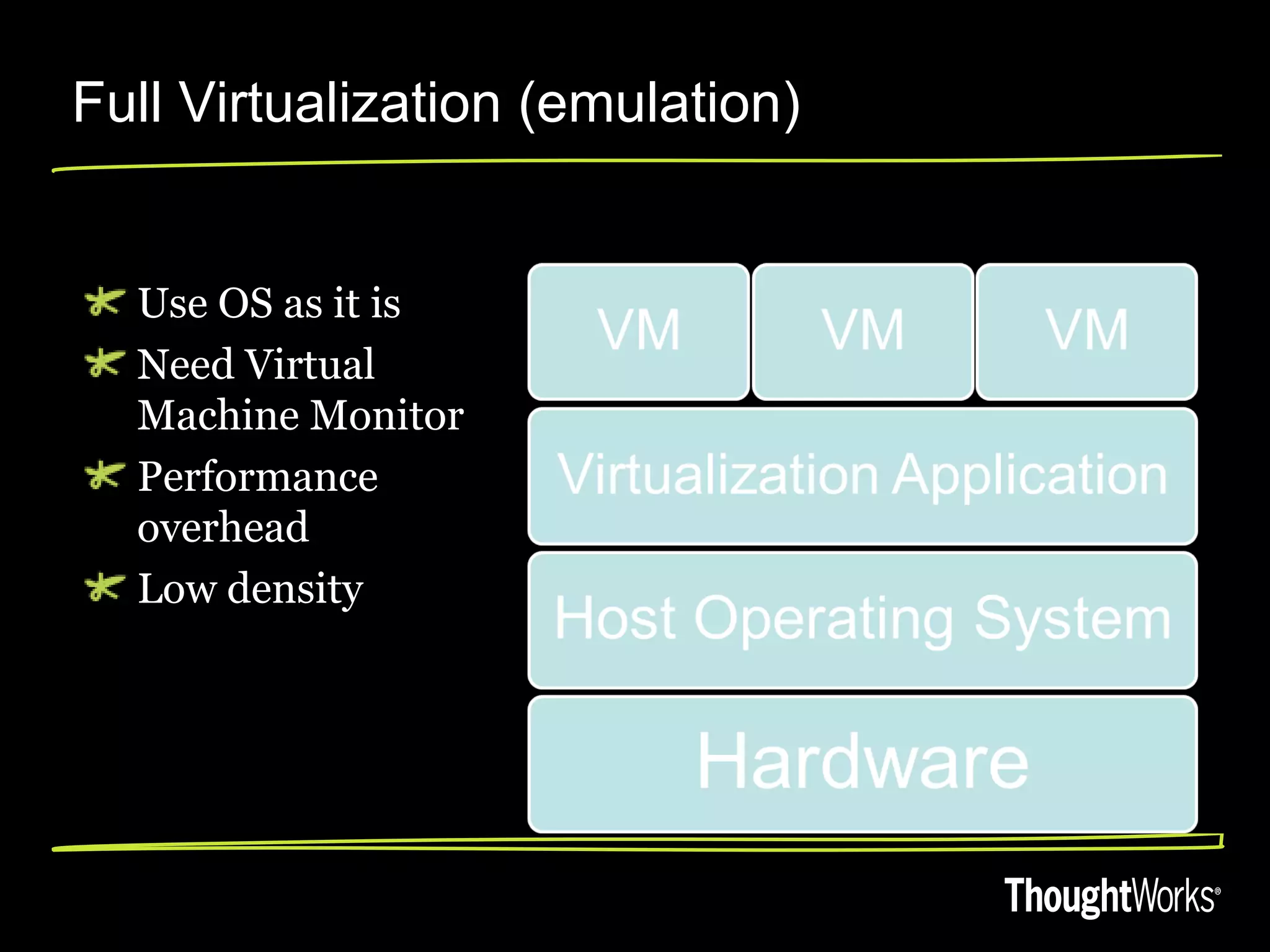
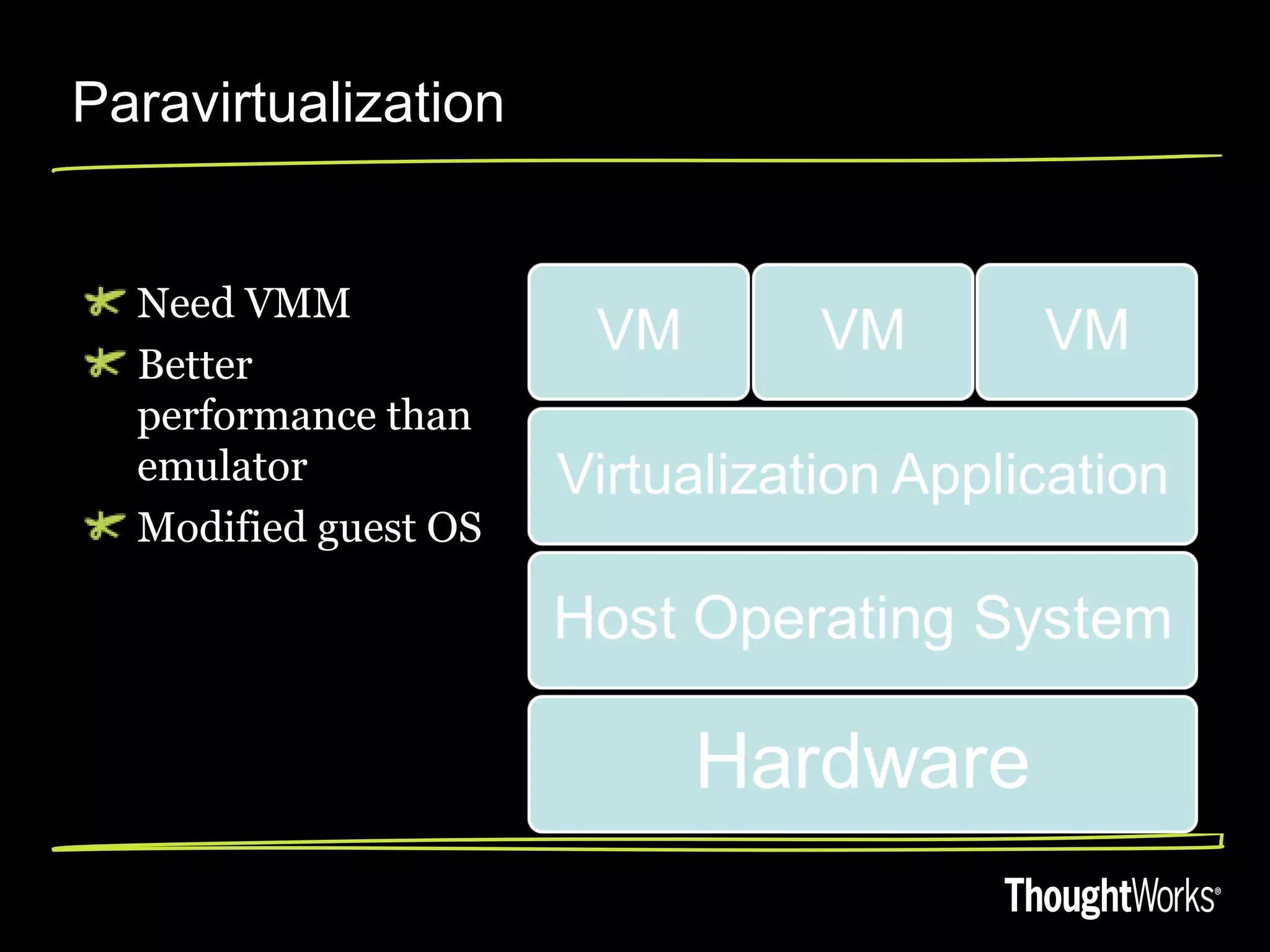
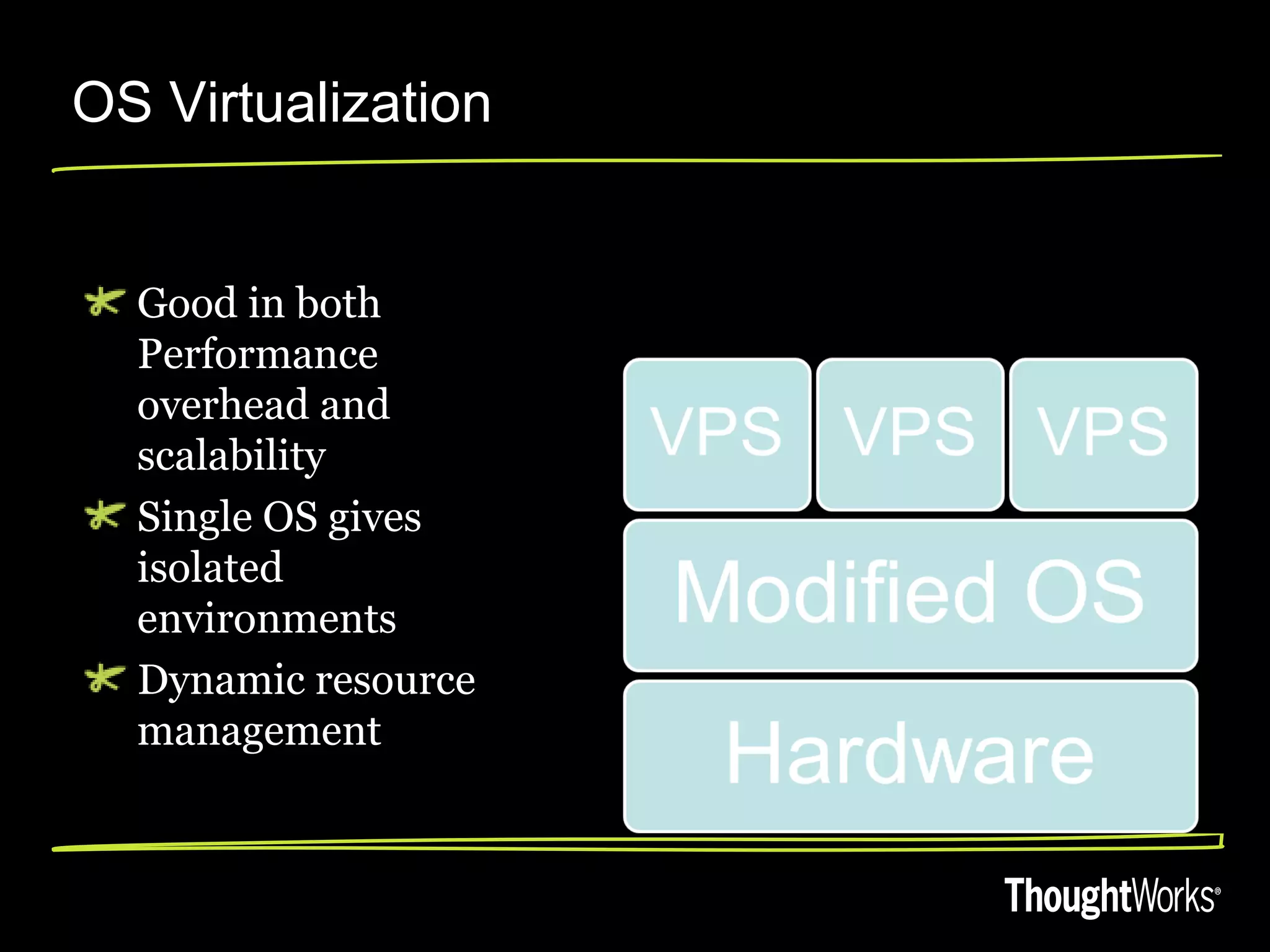
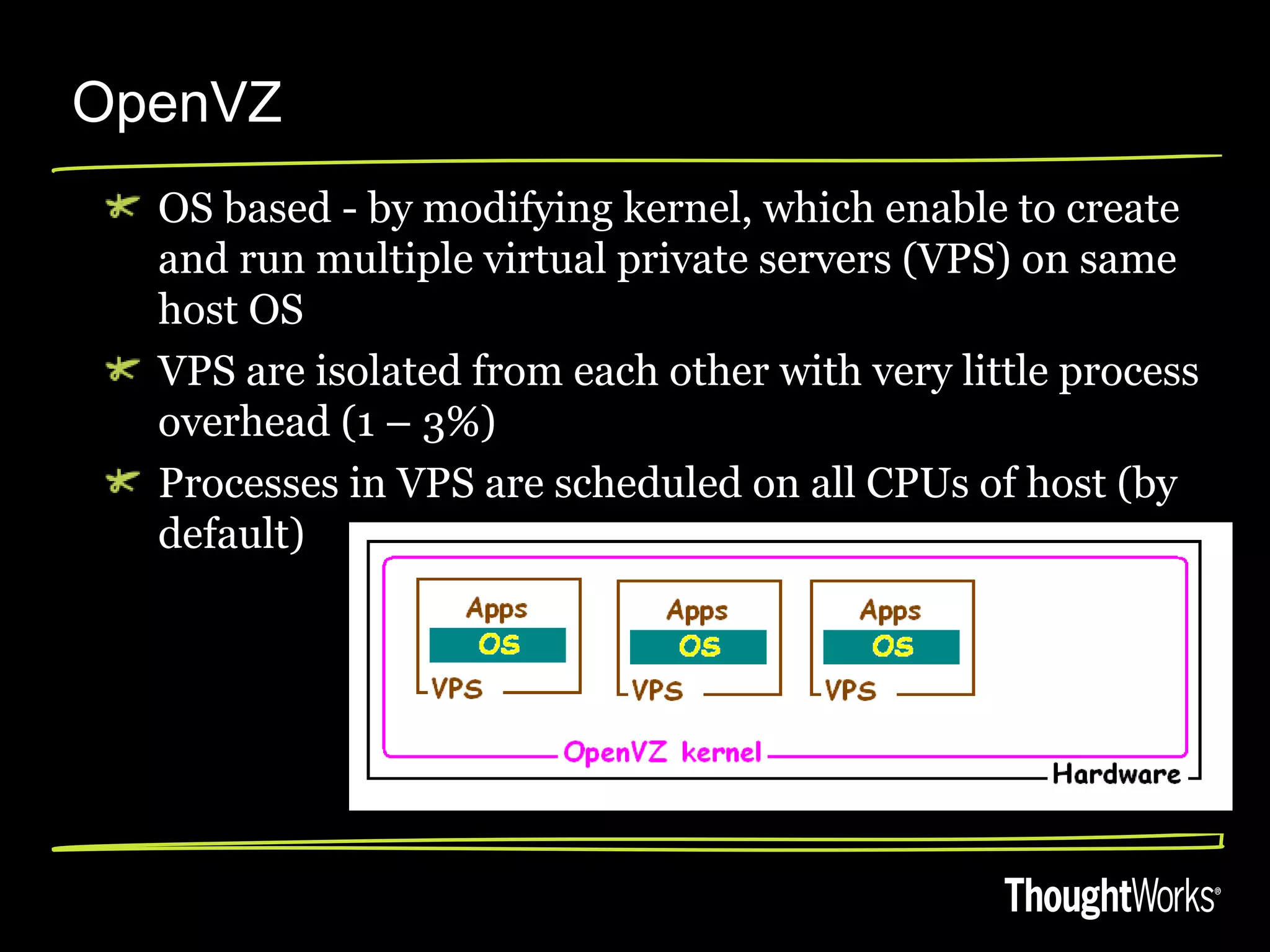
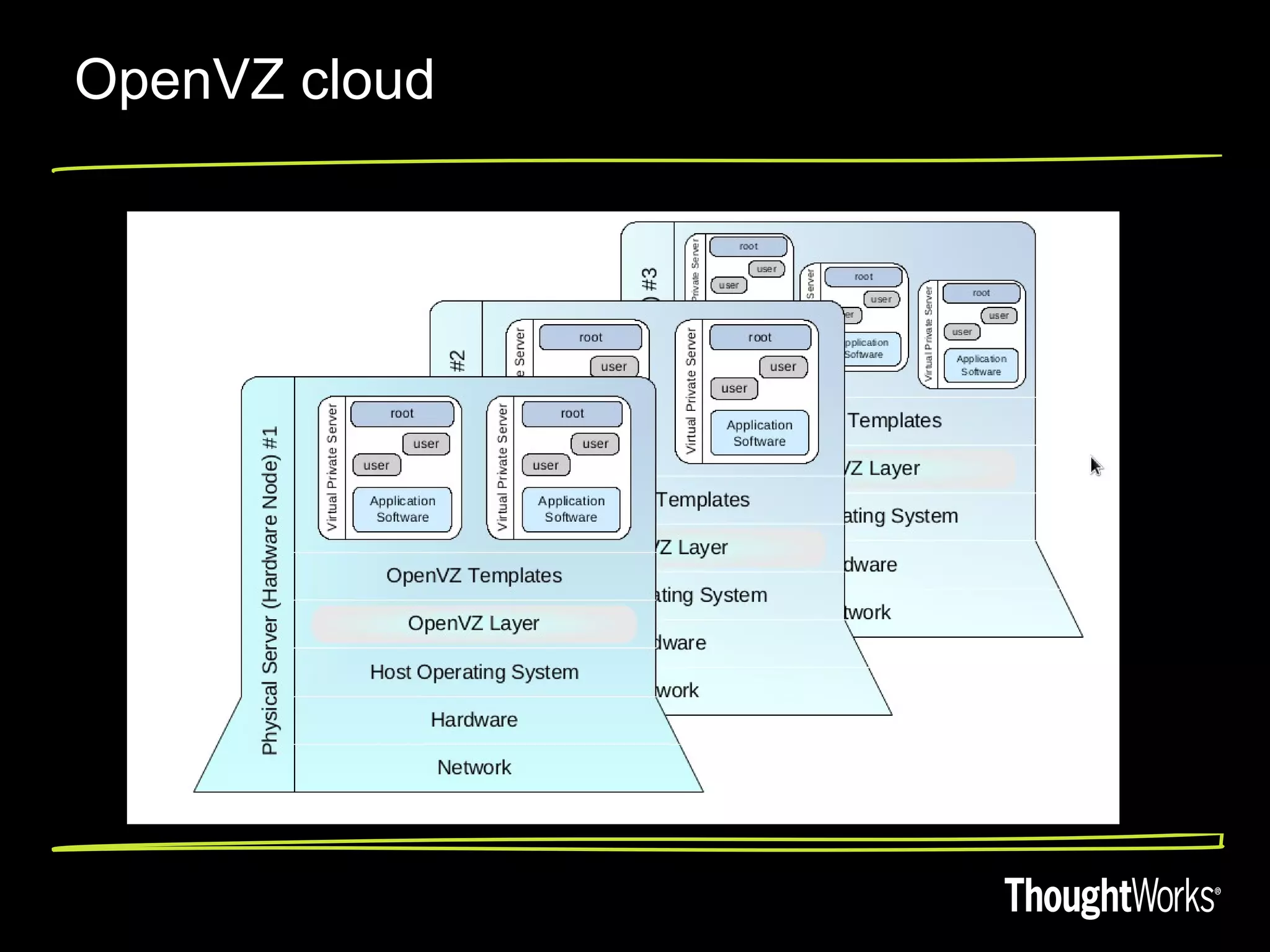
The document discusses high performant virtualization using OpenVZ. It provides an overview of different virtualization options including full virtualization, paravirtualization, and OS virtualization. It then describes OpenVZ, which uses OS-level virtualization by modifying the Linux kernel to create isolated virtual private servers on a single host OS with low overhead of 1-3%. The document outlines some limitations of OpenVZ like requiring a similar kernel, and lists features like dynamic resource management, fast provisioning of VPS, and ability to exceed allocated resources. It discusses using OpenVZ to build a private cloud with benefits like reduced hardware costs, dynamic scaling, and easy live migration between physical servers.