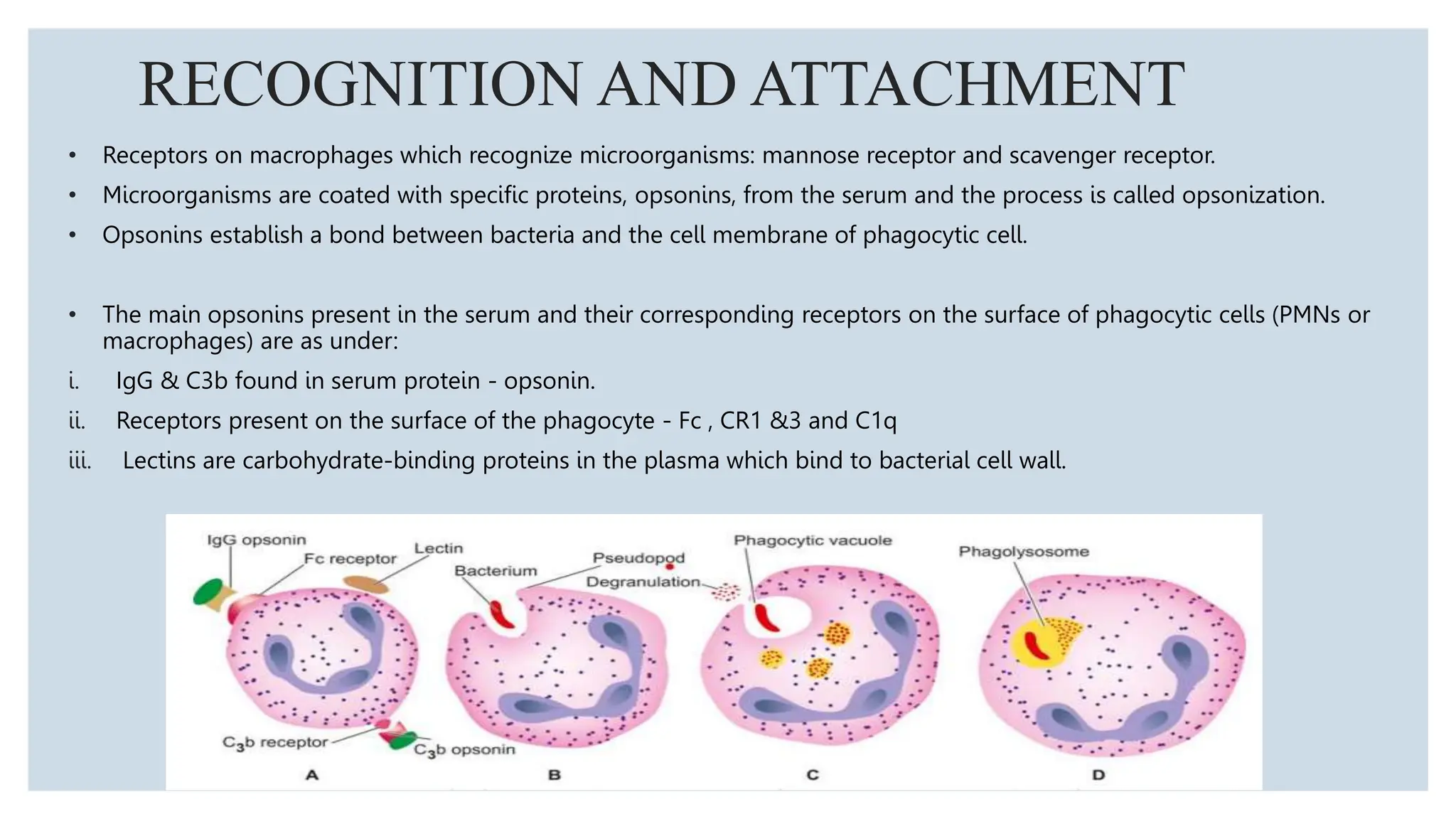
Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cells and form the first line of defense against pathogens. They are formed in the bone marrow through a process called granulopoiesis regulated by G-CSF and migrate to sites of infection. Neutrophils phagocytose and kill microbes via oxidative and non-oxidative mechanisms. Disorders can cause quantitative or qualitative neutrophil defects, resulting in increased susceptibility to infection. Periodontal disease is more severe and widespread in patients with neutrophil disorders due to impaired host response and bacterial modulation of neutrophil functions.

























![DISEASE PMN ABNORMALITY CLINICAL FEATURES
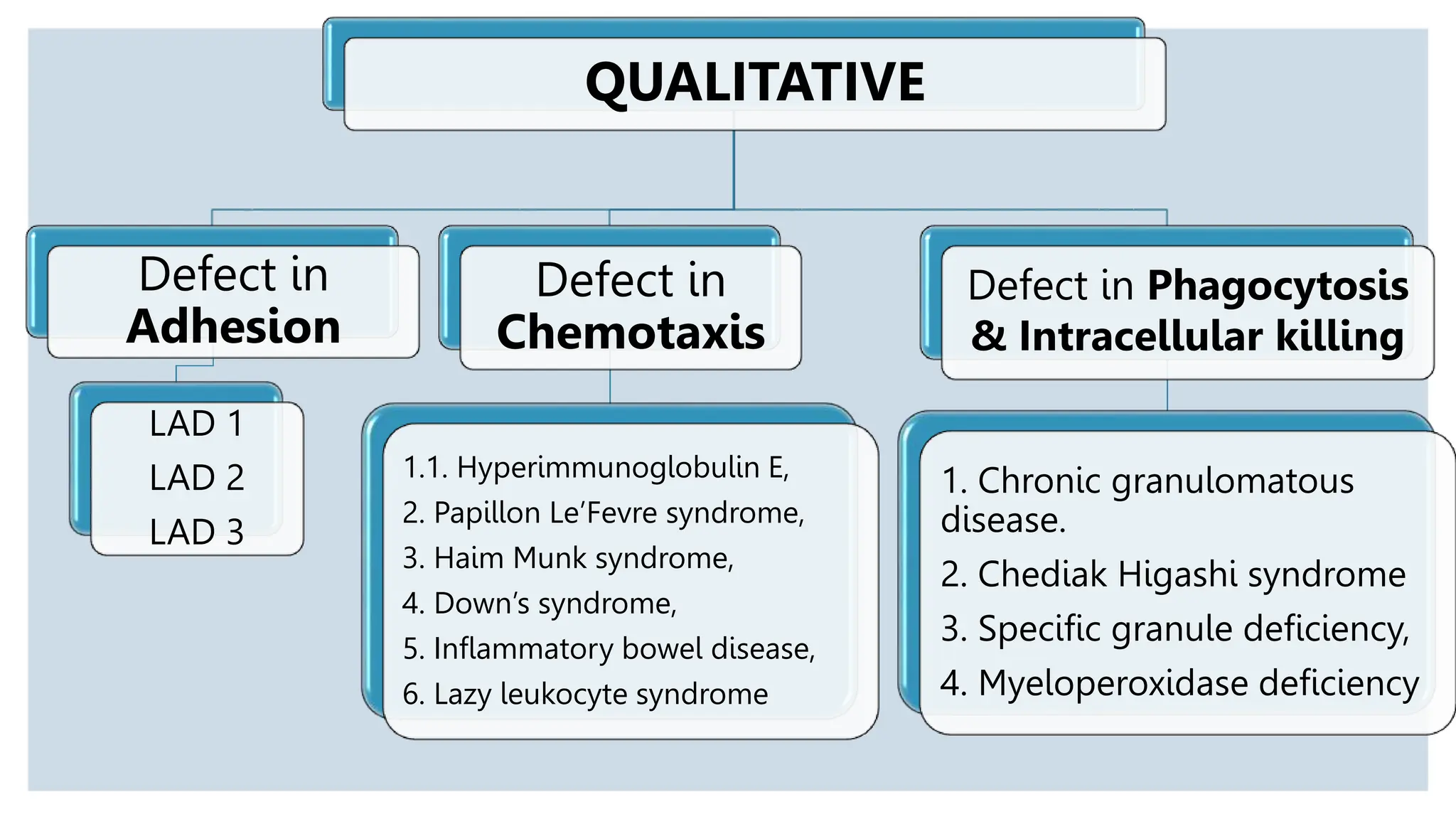
HYPERIMMUNOGLOBULIN E /
JOB’S SYNDROME
1. Increased levels of serum IgE
2. Reduced chemotaxis
1. Skin ‘‘cold’’ abscesses,
2. pneumonia,
3. deep-set eyes,
4. oral ulcerations/gingivitis
HAIM-MUNK SYNDROME 1. Mutations of a gene (known as
cathepsin C [CTSC]) located on
the long arm of chromosome 11
1. Red, scaly thickened patches of skin on the
palms of the hands and soles of the feet .
2. Frequent pyogenic skin infections.
3. Overgrowth of the fingernails and toenails.
4. Degeneration of the periodontium
LAZY LEUKOCYTE SYNDROME 1. Affect both quality and quantity
of neutrophils.
2. Defective chemotaxis along with
neutropenia is seen.
1. Destruction of bone and early tooth loss.
2. Fever skin abscess, gingivitis, periodontitis
DOWNS SYNDROME 1. Endo - lack of lip seal, tongue
thrust, malocclusion, oral
hygiene
2. Exo - neutrophil, phagocytosis,
chemo intracellular killing
(Newman & Carranza 10th edition )
1. The high prevalence and increased severity of
periodontal destruction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmnsinperio-231210042810-c8fdc825/75/ROLE-OF-NEUTROPHILS-IN-HEALTH-DISEASE-pptx-28-2048.jpg)











