This document discusses the rod cutting problem and its solution. It contains:
1) An introduction and presentation by three students with their IDs.
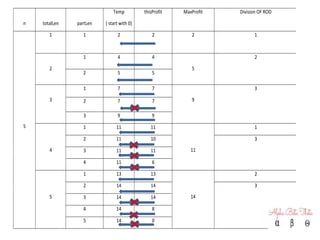
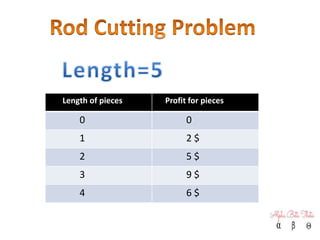
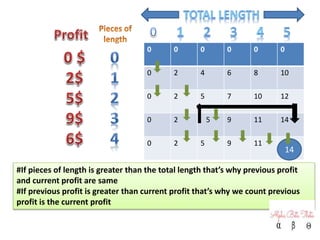
2) An explanation of the rod cutting problem with a table showing length, profit, and total profit.
3) Pseudocode for the recursive solution to calculate maximum profit by cutting a rod into pieces of different lengths.
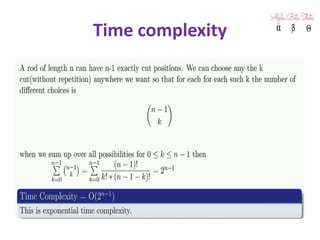
4) Analysis of the time complexity of the recursive solution as O(n^2).





![Pseudo Code
int priceOfLen[ ] = {0, 2, 5, 9, 6};
int maxProfit( n )
{
for (totalLen 1 to n)
{
tmp 0;
for (partLen 1 to totalLen)
{
thisProfit priceOfLen[partLen] + maxProfitOfLen[totalLen - partLen];
if (tmp < thisProfit)
{
tmp thisProfit;
partLenOfLen[totalLen] partLen;
}
}
maxProfitOfLen[totalLen] tmp;
}
return maxProfitOfLen[n];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rod-cutting-dp-191123145232/85/Rod-Cutting-Problem-8-320.jpg)
![Void Divisions( n )
{
while (n > 0)
{
print partLenOfLen[n] ;
n n - partLenOfLen[n];
}
}
Pseudo Code For Knowing The How We Have To Cut The Rod
0 1 2 3 4 5
priceOfLen[ ]
maxProfitOfLen[ ]
partLenOfLen[ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rod-cutting-dp-191123145232/85/Rod-Cutting-Problem-9-320.jpg)