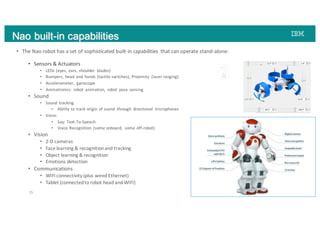
The document discusses advancements in robotics powered by machine learning, highlighting different models and applications of robots like NAO in various fields, from eldercare to retail. It details NAO's capabilities, software environment, and the potential for creating cognitive agents using IBM's Watson technology to enhance human-robot interaction and automate tasks. The integration of AI systems enables robots to develop expertise through continuous learning, aiding in various functions without replacing human roles.