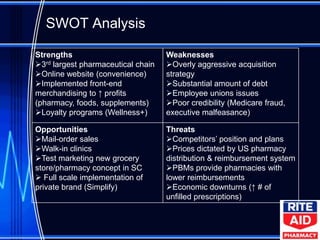
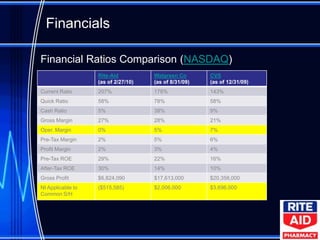
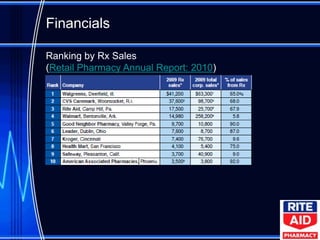
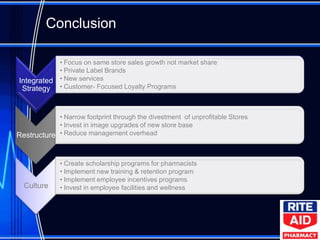
The document provides a case analysis and recommendations for Rite Aid pharmacy. It recommends that Rite Aid focus on same-store sales growth rather than market share through private label brands, new services, and customer loyalty programs. It also recommends restructuring by narrowing Rite Aid's store footprint, upgrading new stores, and reducing overhead. Additionally, it recommends improving company culture by creating scholarship programs for pharmacists and implementing new training, retention, and incentive programs for employees.