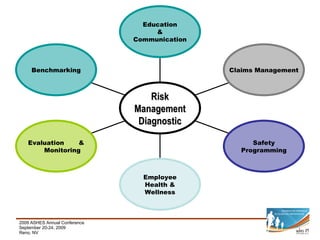
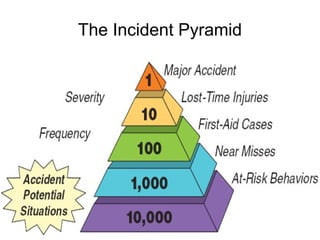
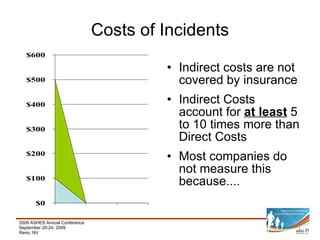
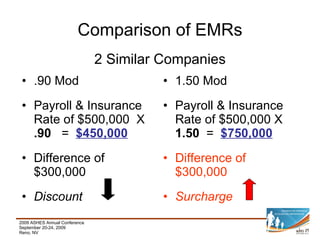
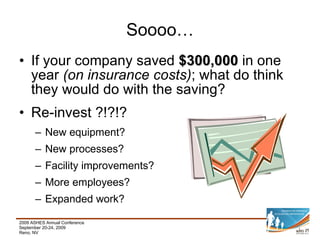
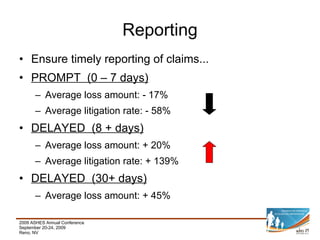
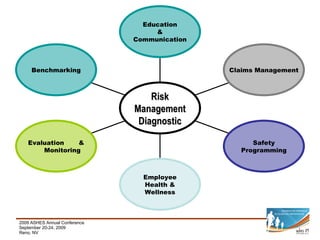
This document provides a summary of key aspects of risk management for a company, including safety programming, employee health and wellness, claims management, education and communication, evaluation and monitoring, and benchmarking. It discusses the importance of these areas and offers recommendations. Specific topics covered include case studies of workplace incidents, indirect costs of incidents, workers' compensation insurance and experience modification rates, components of an effective safety plan, types of wellness programs, employee screening, and how to effectively benchmark performance.








































![Questions / Thank You Roger Paveza 847.463.7223 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riskmanagementdiagnosticashes2009-12502752571367-phpapp03/85/Risk-Management-Diagnostic-Ashes2009-54-320.jpg)