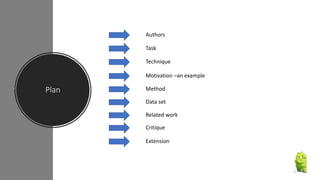
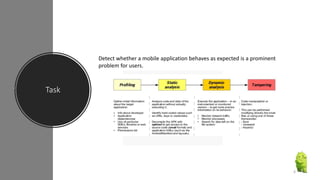
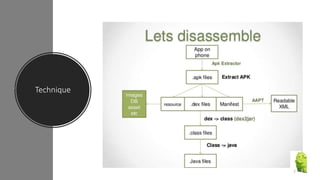
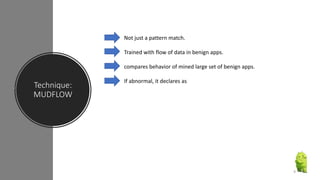
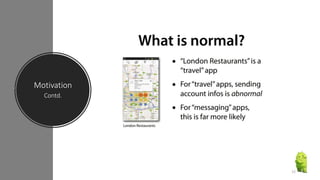
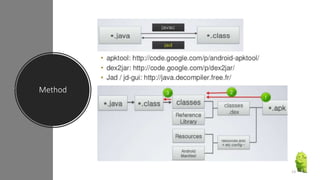
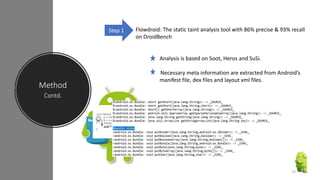
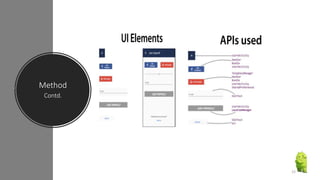
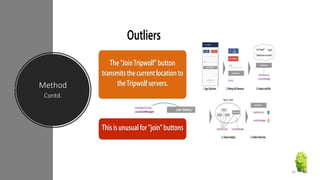
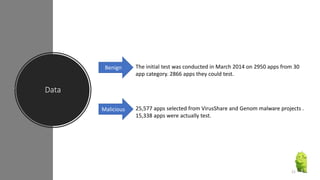
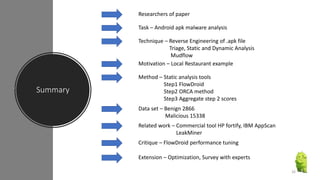
The document discusses a research paper on detecting abnormal usage of sensitive data in mobile applications, focusing on Android APK malware analysis techniques that employ static and dynamic analysis methods like Mudflow and FlowDroid. The method is validated against a dataset of benign and malicious apps, highlighting the challenges of false positives and the need for performance optimization. Suggestions for extensions include improving analysis for varied app sizes and conducting a comparison with commercial tools.