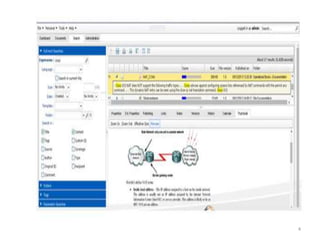
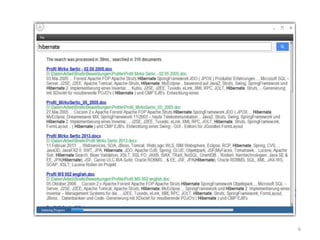
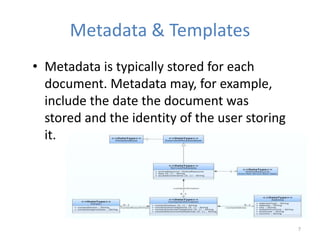
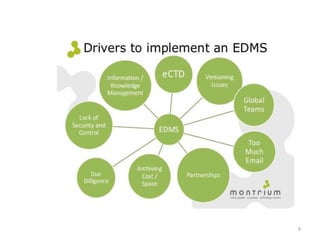
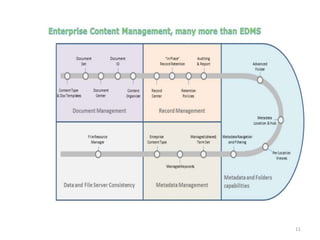
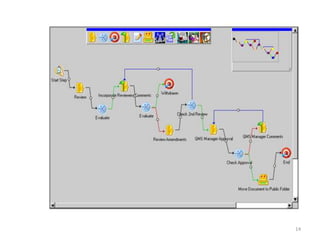
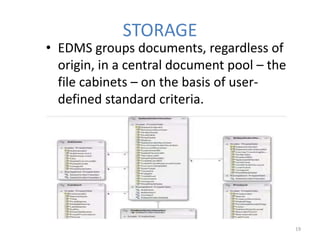
This document discusses various topics relating to electronic document management, archiving, and retrieval. It covers document retrieval features like full-text searches and task-specific profiles. It also discusses full-text indexing, metadata, version control, document searching using metadata fields, record retention policies, workflows, storage methods like hierarchical storage management, autonomous file cabinets for archiving, backup methods, and how electronic document management systems can help organizations streamline document handling and reduce costs.