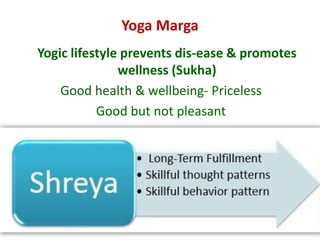
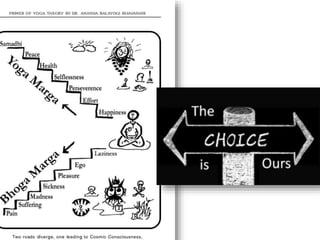
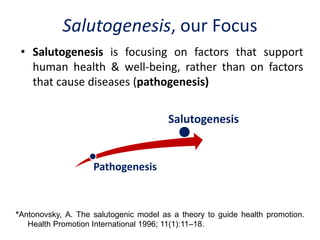
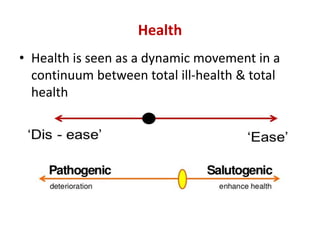
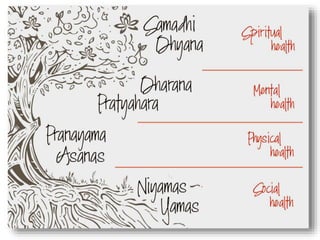
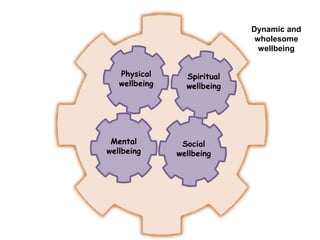
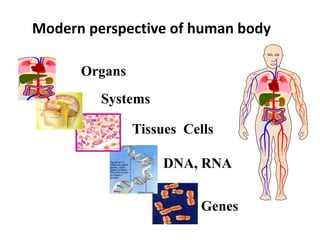
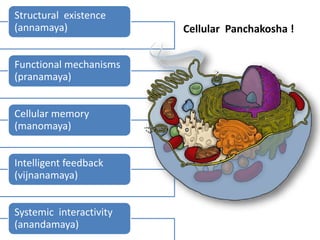
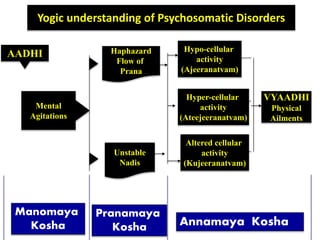
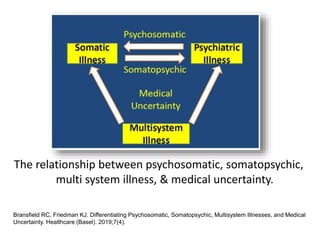
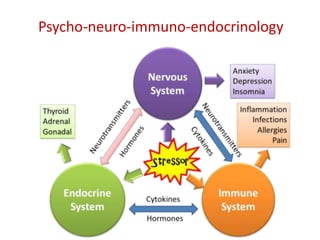
The presentation by Dr. Meena Ramanathan at the conference on yoga emphasizes the importance of integrating salutogenesis in yoga therapy, which focuses on promoting health and well-being rather than merely treating disease. It highlights the multifaceted aspects of yoga, including physical, mental, and spiritual well-being, and the need for a holistic approach to health that incorporates lifestyle, diet, and proper practices. The ultimate goal of yoga therapy is to empower individuals towards optimal health through the teachings and practices of yoga.