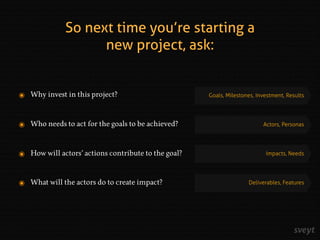
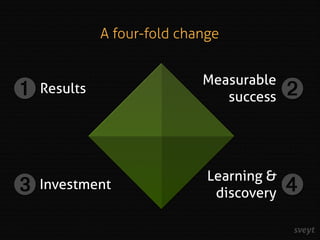
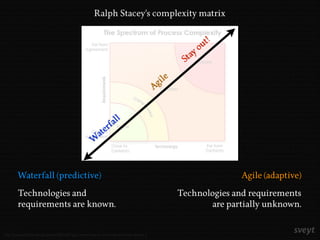
Jakob Persson discusses the importance of shifting project management from a requirements-oriented approach to a results-oriented strategy to improve project success rates, which currently stand at only 16%. He emphasizes the need for clear communication of business goals, realistic expectations, and continuous feedback during project execution, suggesting methodologies like impact mapping and agile project management as effective alternatives. The focus should be on delivering value and addressing business needs rather than merely fulfilling a list of requirements.
























![[slide: WidgetCo HQ]
One beautiful spring morning…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-25-320.jpg)

![[slide: In front of computer]
Susan is researching competitors’ websites.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-27-320.jpg)
![[slide: Stack of documents]
The requirements stack up.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-28-320.jpg)




![de·vel·op·er [dih-vel-uh-per] noun: A person that
converts coffee into code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-33-320.jpg)


















































![[slide: WidgetCo HQ]
One beautiful spring morning…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-86-320.jpg)




![[slide: interview of a person]
WidgetCo makes pet products, did I mention that?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-91-320.jpg)
![[slide: wireframes]
Wireframes were drawn.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-92-320.jpg)
![[slide: presentation]
The agencies made impressive pitches.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-93-320.jpg)
![[slide: happy team]
The agency seemed to love what they did.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-94-320.jpg)
![[slide: enthusiastic person]
Susan’s enthusiasm was also ehm... strong.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-95-320.jpg)
![[slide: person thinking hard]
Analyzing the requirements took some deep thinking.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-96-320.jpg)
![[slide: meeting]
The team had continuous meetings.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-97-320.jpg)
![[slide: effective team]
Finding the requirements that contributed most to
impact took time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-98-320.jpg)
![[slide: champagne, party]
The end result was what everyone had been hoping for.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rowi-prague-131001085041-phpapp02/85/Results-Only-Web-Investments-99-320.jpg)