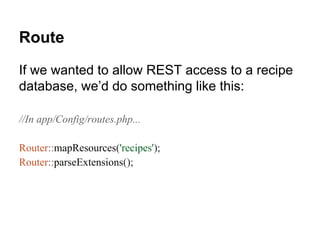
This document discusses how to build RESTful APIs with CakePHP. It explains REST concepts and shows how to configure routes and controllers to support REST actions like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. Code examples are provided for defining routes, controllers that handle REST actions, and modifying views to output different formats like XML. Customizing the default resource mapping with Router::resourceMap() is also covered.