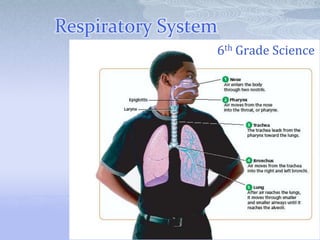
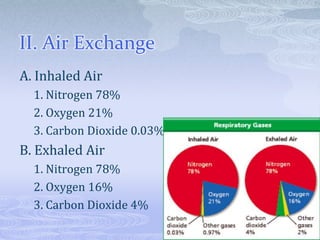
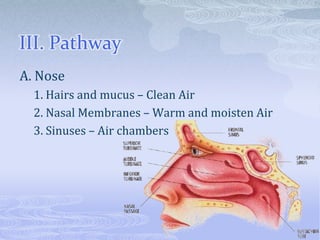
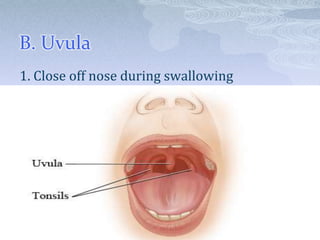
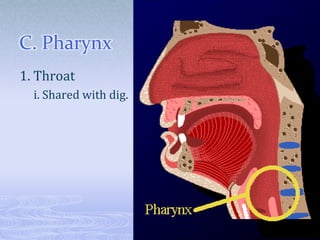
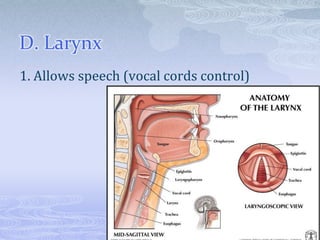
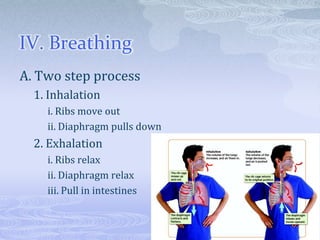
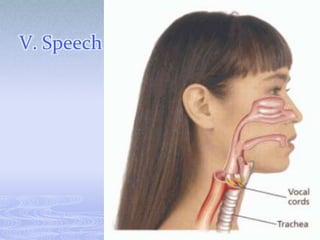
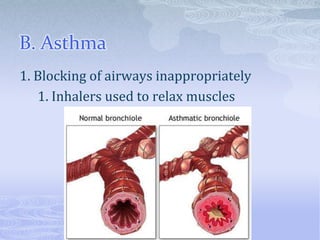
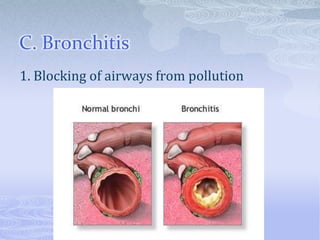
The respiratory system takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide, providing energy for cells. Air moves through the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and into tiny alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. Breathing is a two-step process of inhalation, where the ribs expand and diaphragm contracts, and exhalation, where the ribs relax and diaphragm relaxes. Damage from smoking can cause lung cancer, emphysema and bronchitis due to tar and other chemicals.