The document discusses regulation of respiration, including:
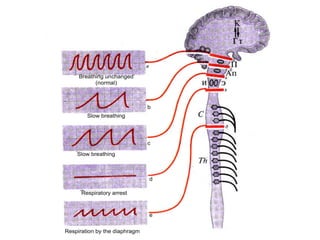
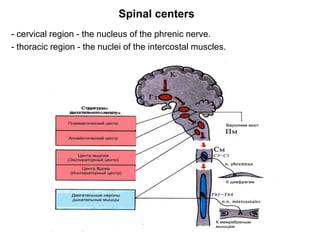
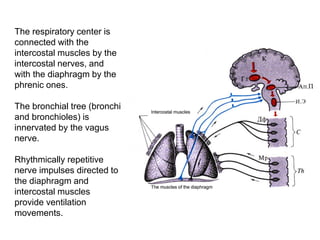
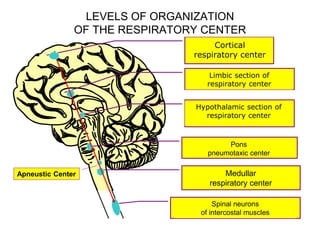
1. The respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata and consists of inspiratory and expiratory neurons that generate rhythmic breathing patterns.
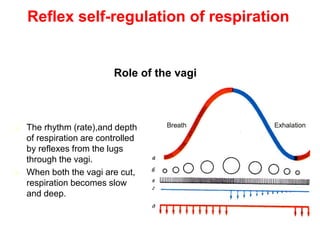
2. Breathing is also regulated by centers in the pons and hypothalamus as well as reflexes from lung stretch receptors, irritant receptors, and J-receptors in the lungs.
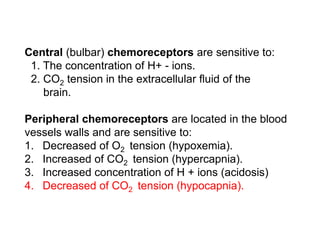
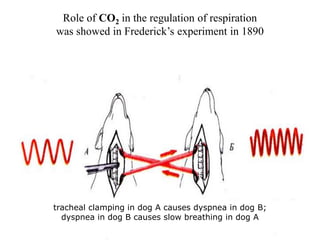
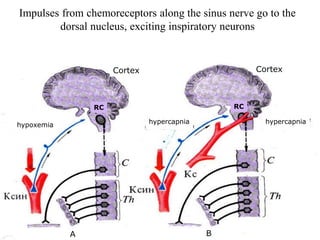
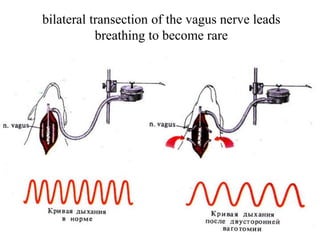
3. The tone and rhythm of breathing is controlled by chemoreceptors sensitive to oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen ions and the autonomic nervous system through the vagus nerves.