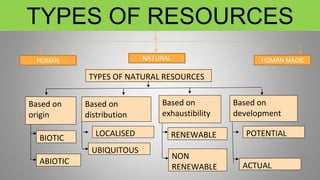
This document discusses different types of resources including natural, human, and human-made resources. It defines a resource as anything that can satisfy a need and has utility and value. Resources can be natural like land, air and water, human like skills and knowledge, or made by humans using natural resources. The document outlines that resources are unequally distributed based on terrain, climate and altitude. It emphasizes that human beings are the most important resource because they generate demand, give utility to other resources, and can develop new resources through ideas, knowledge and technology. The document also discusses renewable vs. non-renewable resources and our duties to conserve resources and environment.