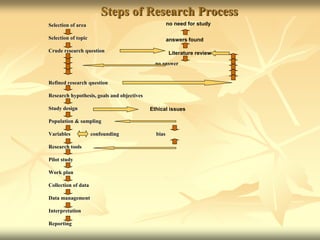
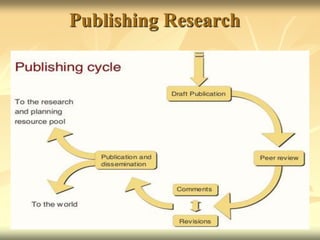
The document outlines the research process and provides guidance on selecting topics and formulating research questions and objectives. It discusses defining research, reality, and ways of defining problems. The key steps of the research process include selecting an area and topic, developing research questions and hypotheses, study design, data collection and analysis, and reporting findings. Good topics are interesting, researchable, significant, manageable, and ethical. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.