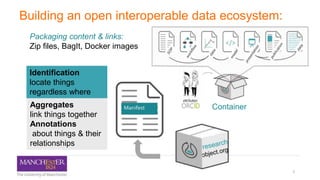
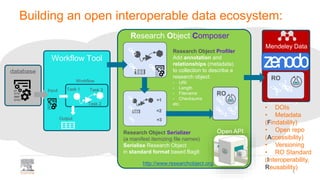
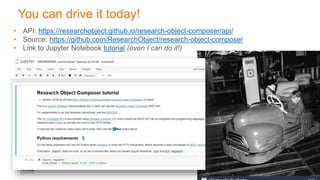
The document discusses the Research Object Composer, a tool designed to enhance the accessibility and interoperability of biomedical data by following FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable). It emphasizes the need for standardized data management practices and outlines use cases in fields like earth sciences and chemistry. The composer acts as a microservice aiding in the construction and validation of research objects, with a focus on facilitating collaborative research and data sharing.