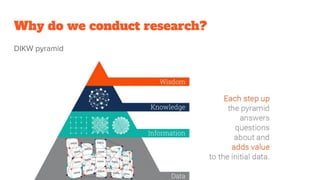
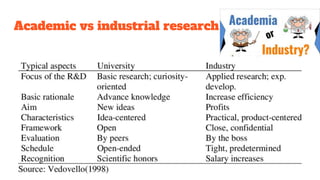
Research is a systematic process of exploring unanswered questions or issues through collecting and analyzing data. It aims to increase understanding and make informed decisions. There are two main types of research - basic research which develops new theories, and applied research which evaluates actions for industry or practice. Research methods can be qualitative using open-ended questions, or quantitative using measurable variables. Good research is systematic, logical, replicable, and has clearly defined objectives and appropriate methodology. Key factors for a good research topic include being novel, relevant, feasible, researchable, and ethical. A master's thesis demonstrates knowledge in the field while a PhD thesis makes an original contribution.