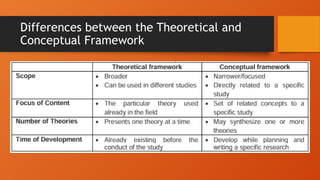
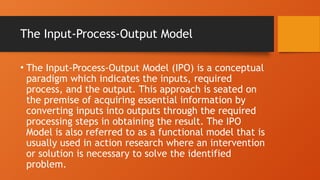
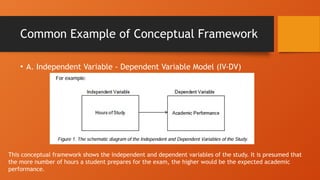
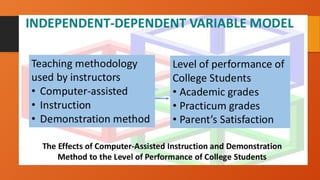
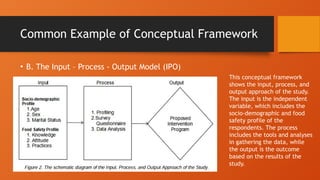
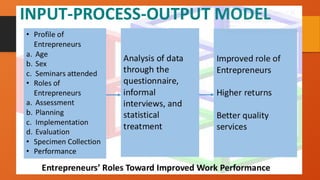
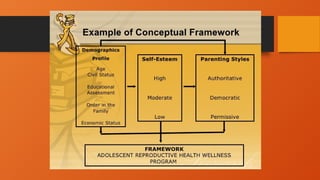
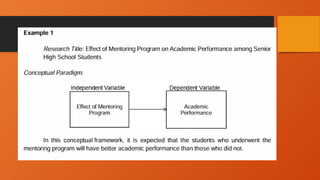
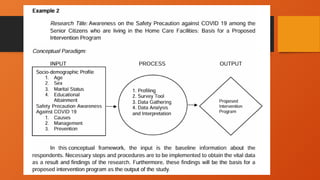
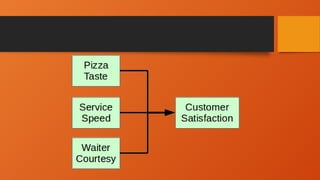
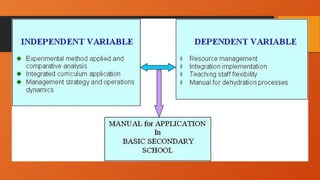
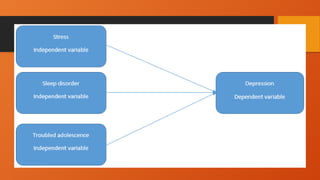
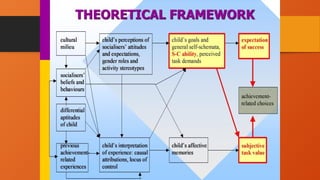
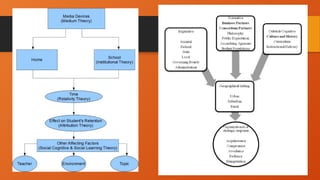
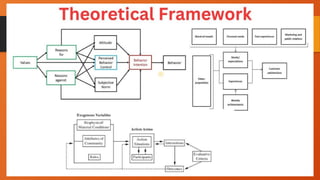
The document outlines the importance of research frameworks, distinguishing between theoretical and conceptual frameworks that guide researchers in formulating questions and structuring studies. It explains the similarities and differences between these frameworks and provides guidelines for developing each, including understanding variables and creating concept maps. Additionally, it introduces the input-process-output (IPO) model as a functional approach in research design.