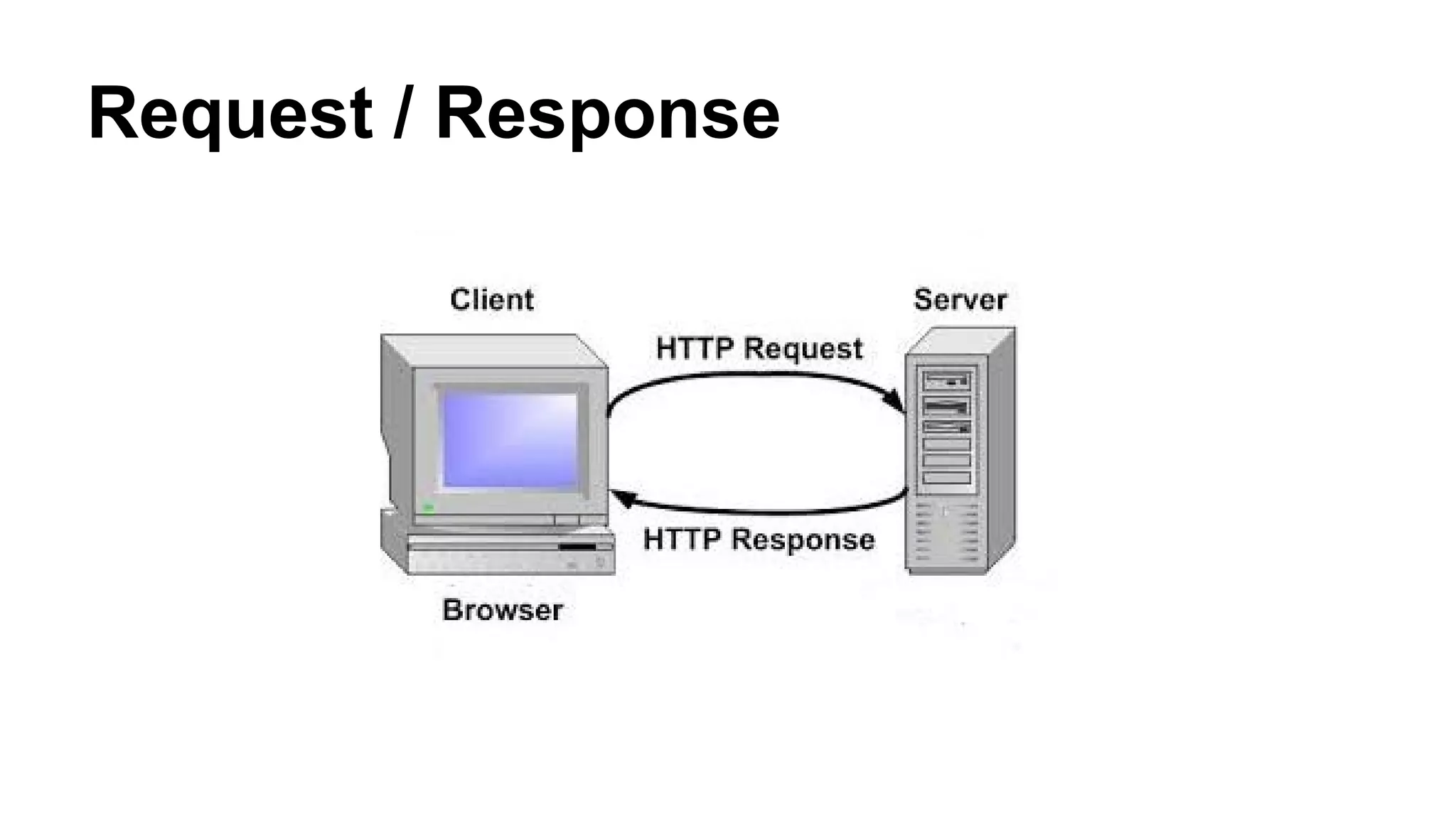
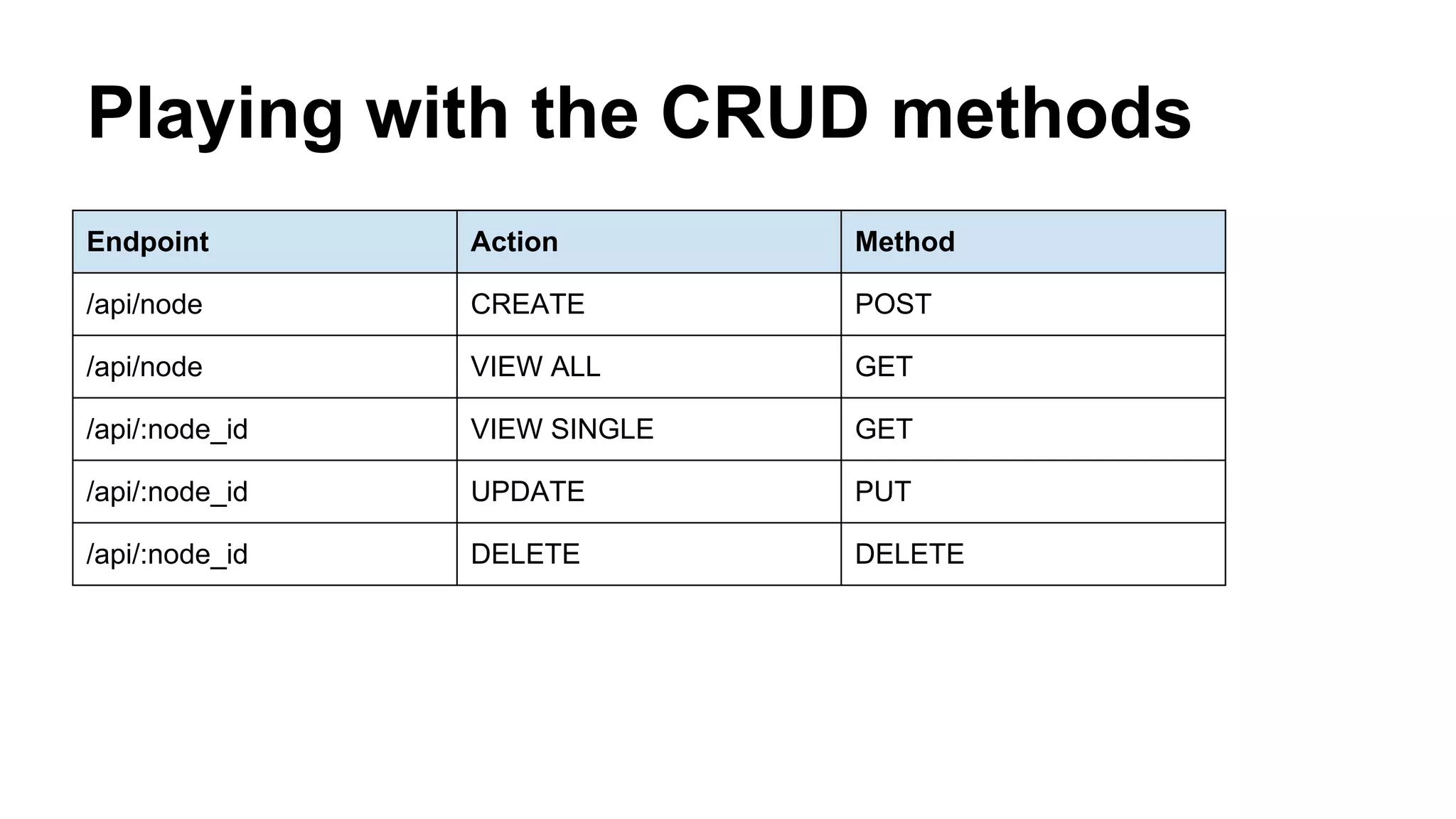
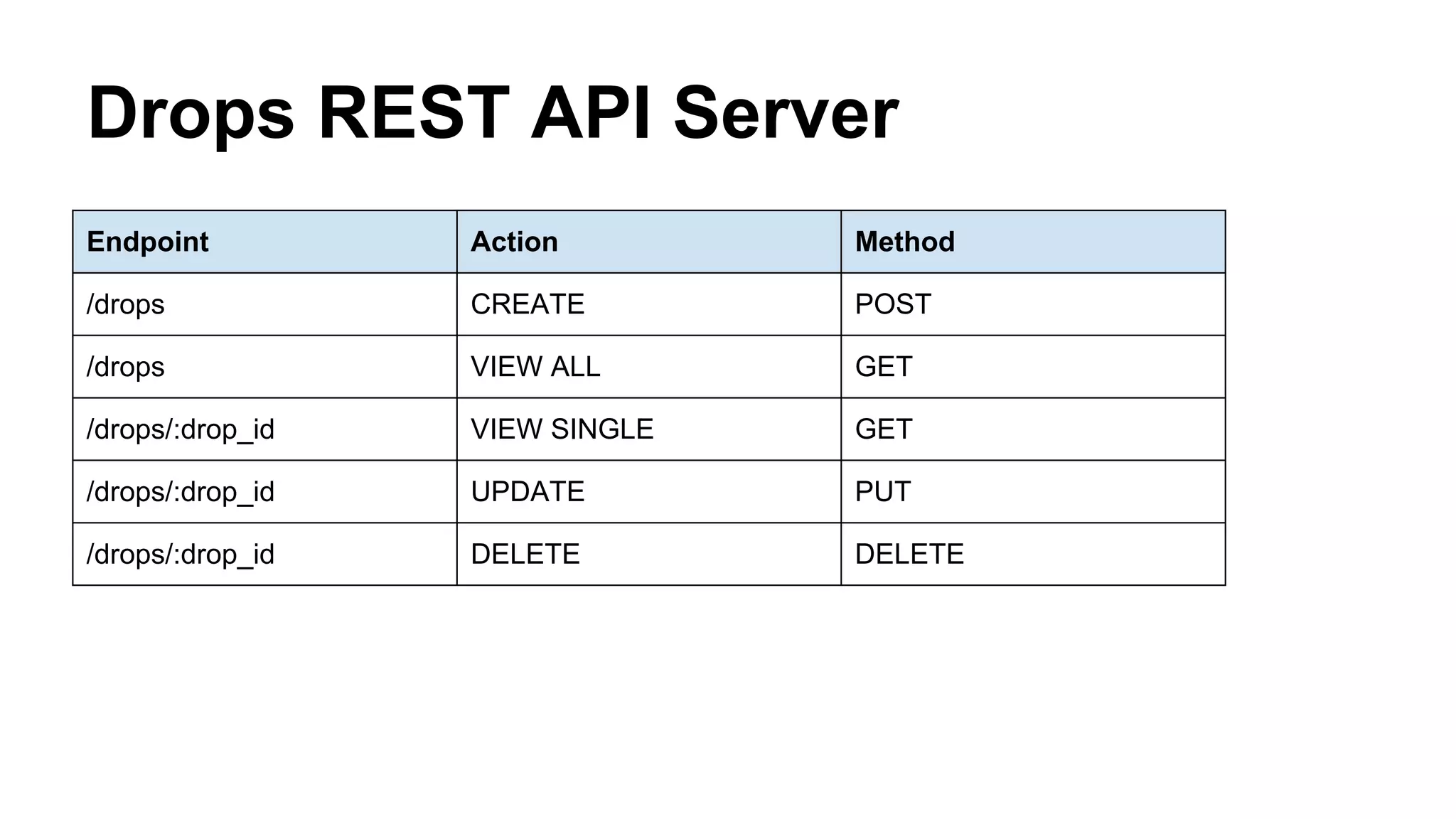
The document discusses building and using RESTful APIs with Drupal. It provides an overview of REST and its benefits, how data can be managed by Drupal as a REST server or client, considerations for building REST APIs, and modules and tools for working with REST in Drupal. The presentation agenda includes explaining REST, reasons to use RESTful APIs, data management paradigms in Drupal, and a demo of managing data both inside and outside of Drupal via REST.