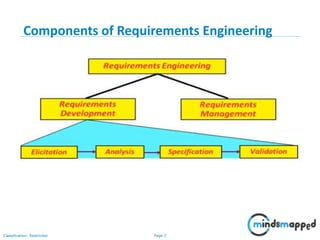
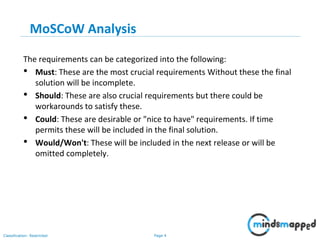
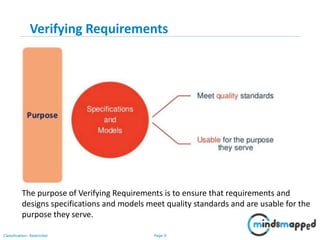
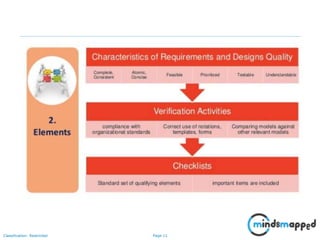
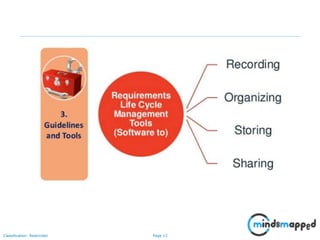
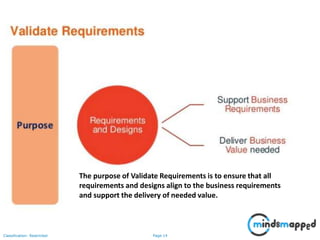
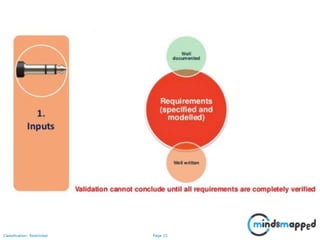
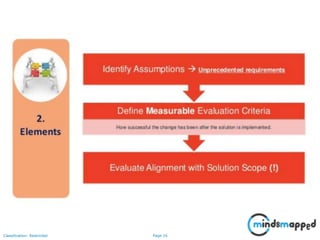
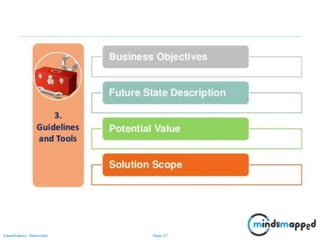
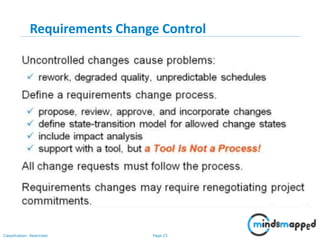
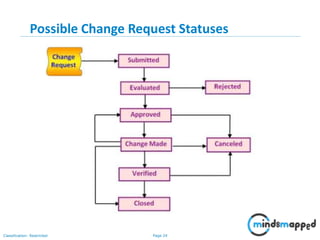
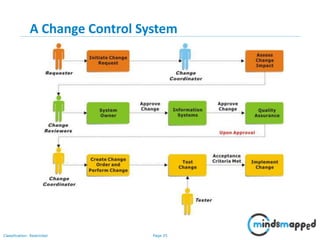
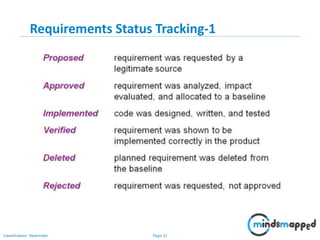
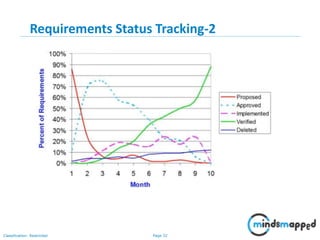
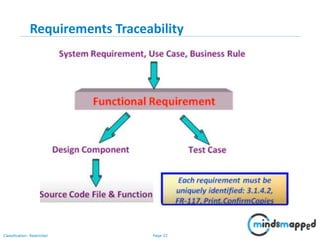
The document outlines key practices in requirements management for business analysts, focusing on techniques like Moscow analysis, time boxing, and voting to prioritize requirements effectively. It emphasizes the importance of verifying and validating requirements to ensure they align with business needs and maintain quality standards. Additionally, it covers practices such as creating a requirements baseline, change control processes, and the use of a requirements traceability matrix.