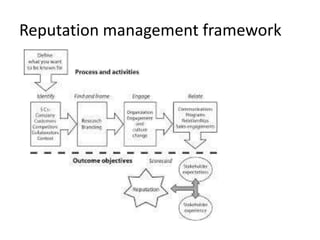
The document discusses reputation management and reputational risk. It defines reputation versus brand, noting that reputation is a measure of trust created by stakeholders, while brands are manufactured by organizations. It also outlines the benefits of a good reputation and presents frameworks for reputation management and reputational risk management. These frameworks identify determinants of reputational risk and ways to manage such risks. The document then provides examples of these frameworks applied to Holcim Vietnam, including stakeholder analysis and typical causes and likelihood of reputation risks.