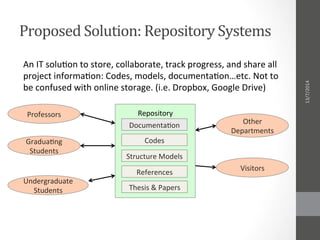
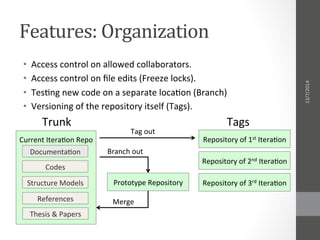
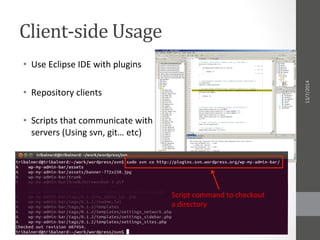
The document proposes a repository system for the Aerospace & Aeronautics Department at Cairo University to improve documentation and sharing of project information for iterative projects like cubesat and n-copter. It highlights the challenges faced due to lack of shared technical aspects and provides a solution that includes collaboration, organization, and sharing features through different online services such as Bitbucket and GitHub. The plan emphasizes the need for training and community involvement to ensure effective use of the repository system.