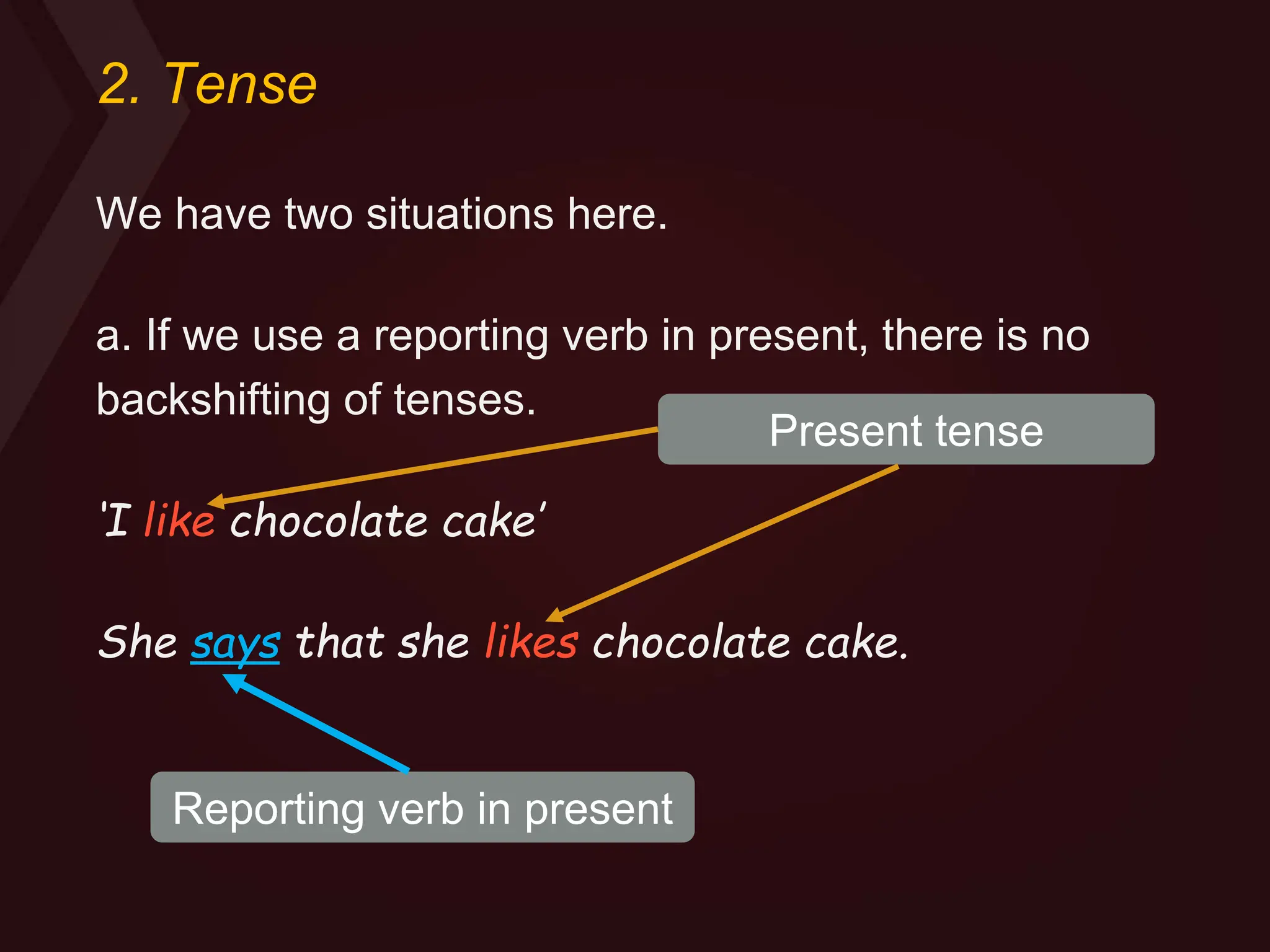
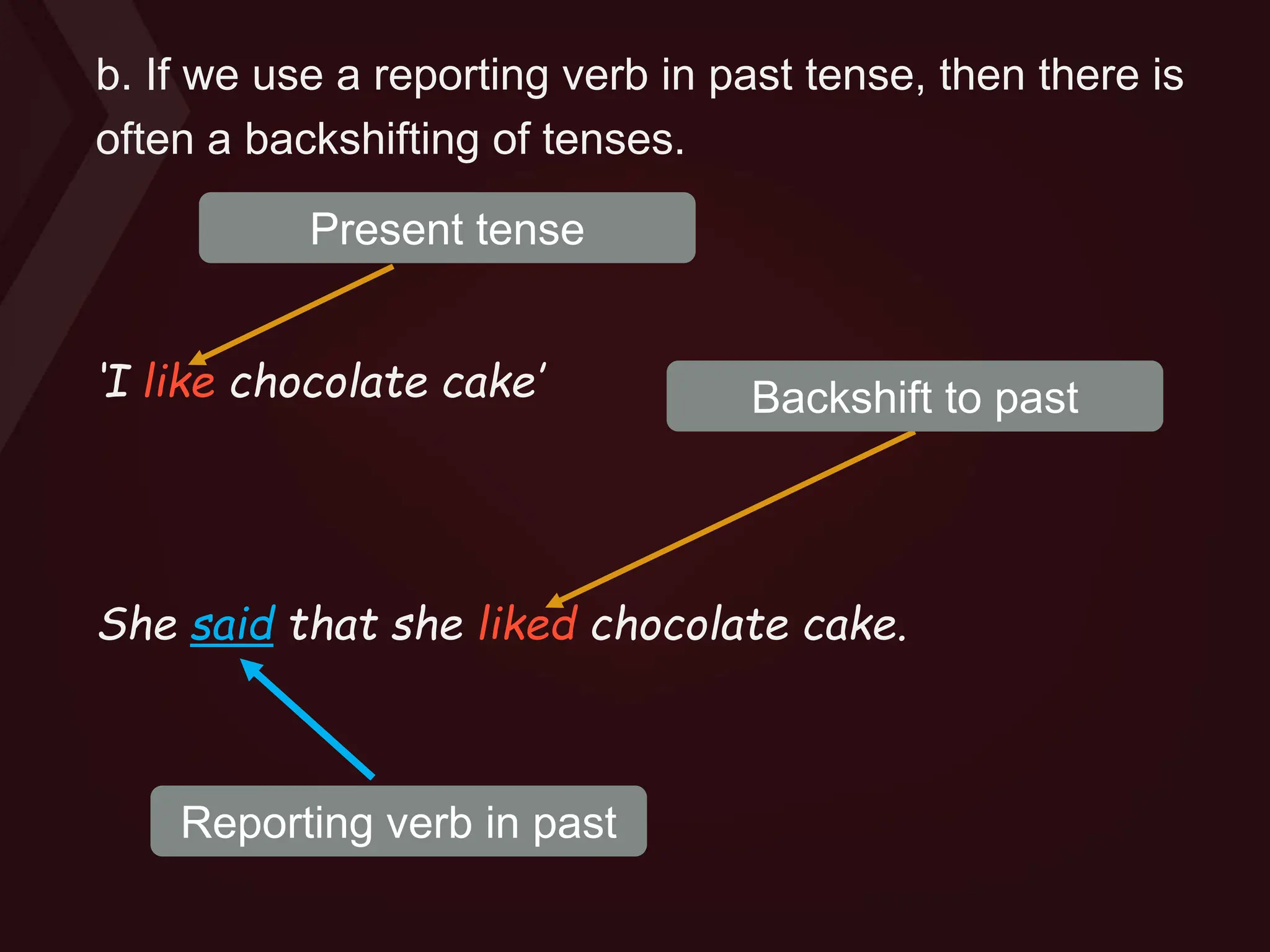
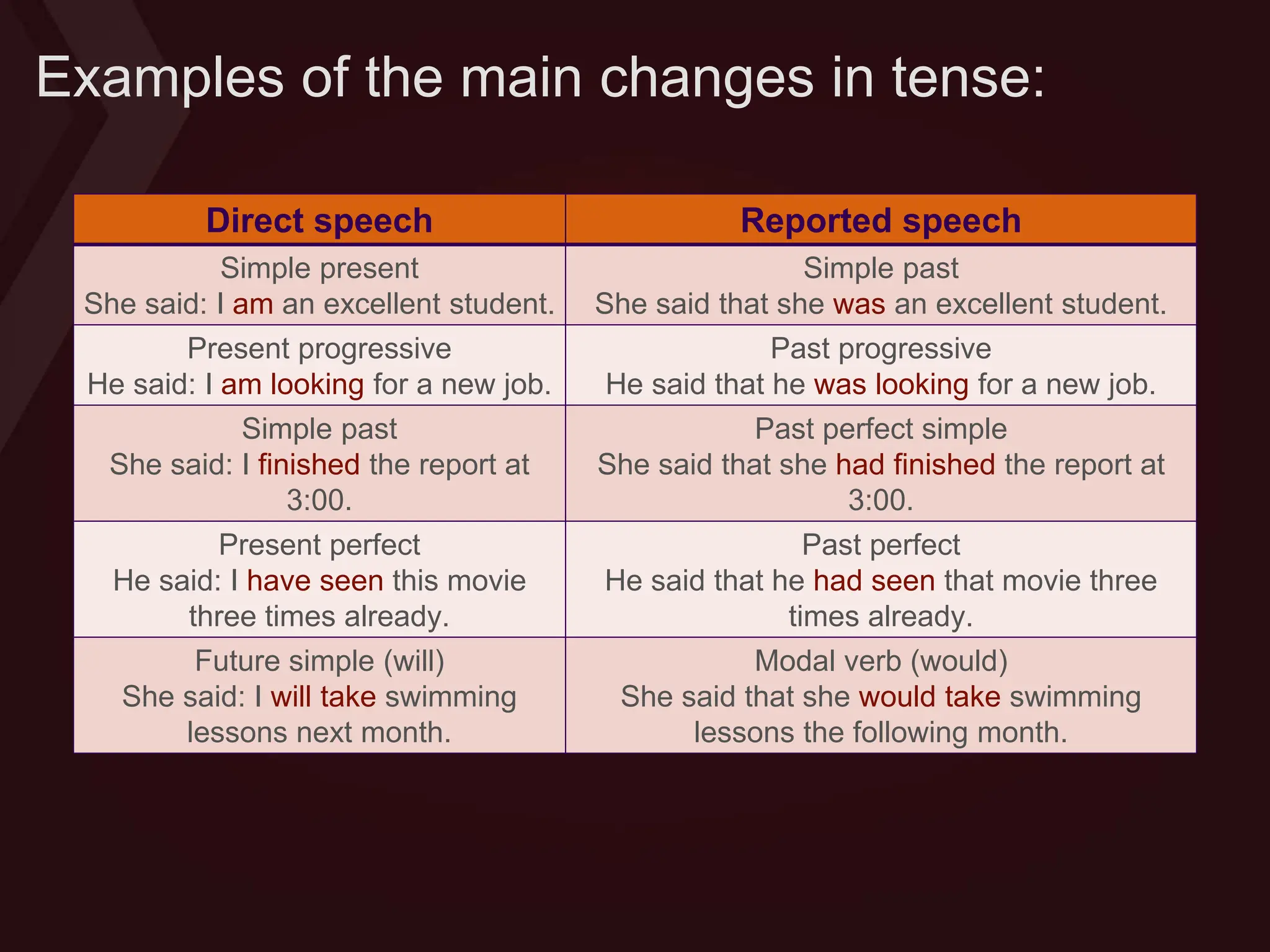
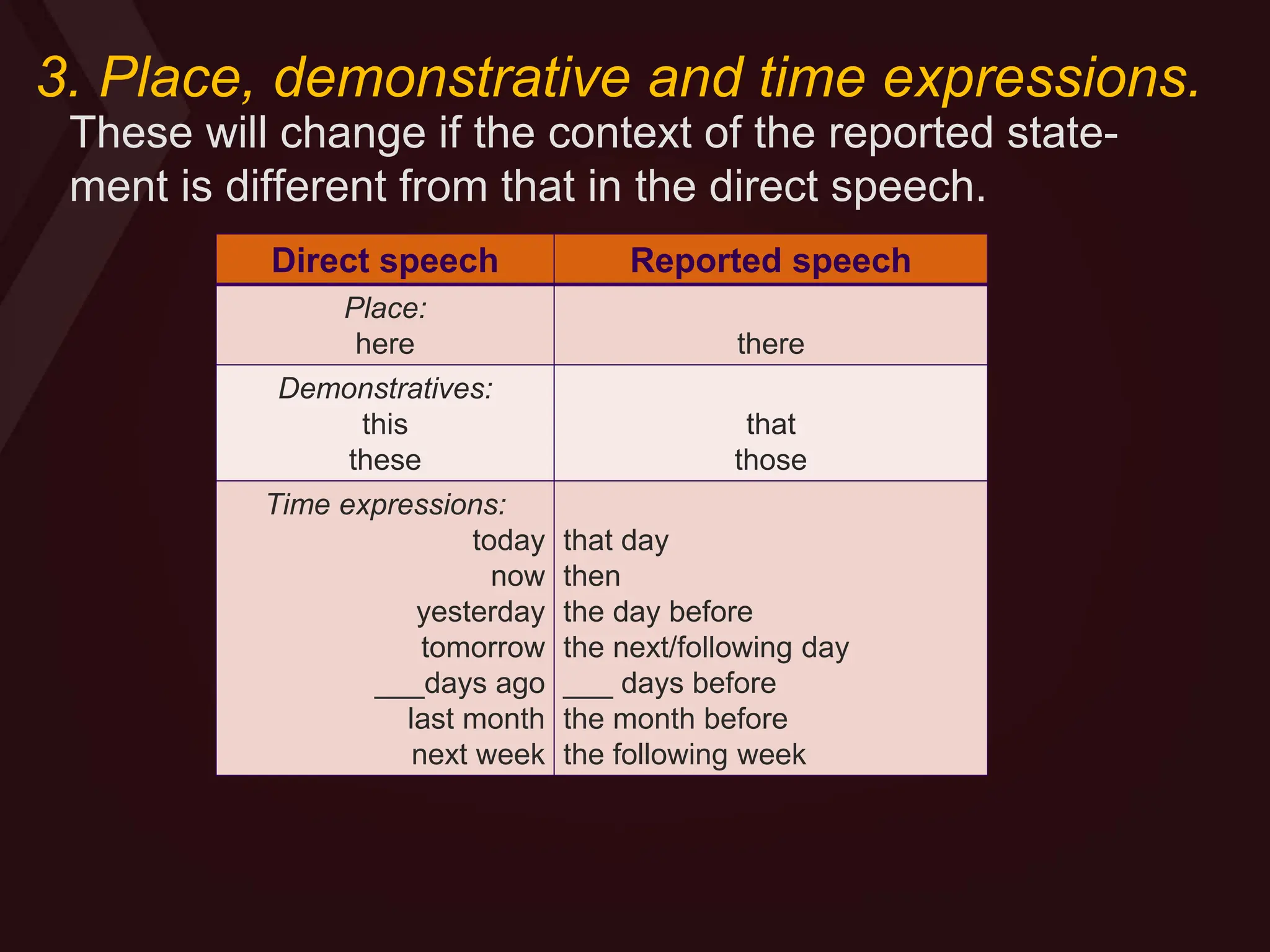
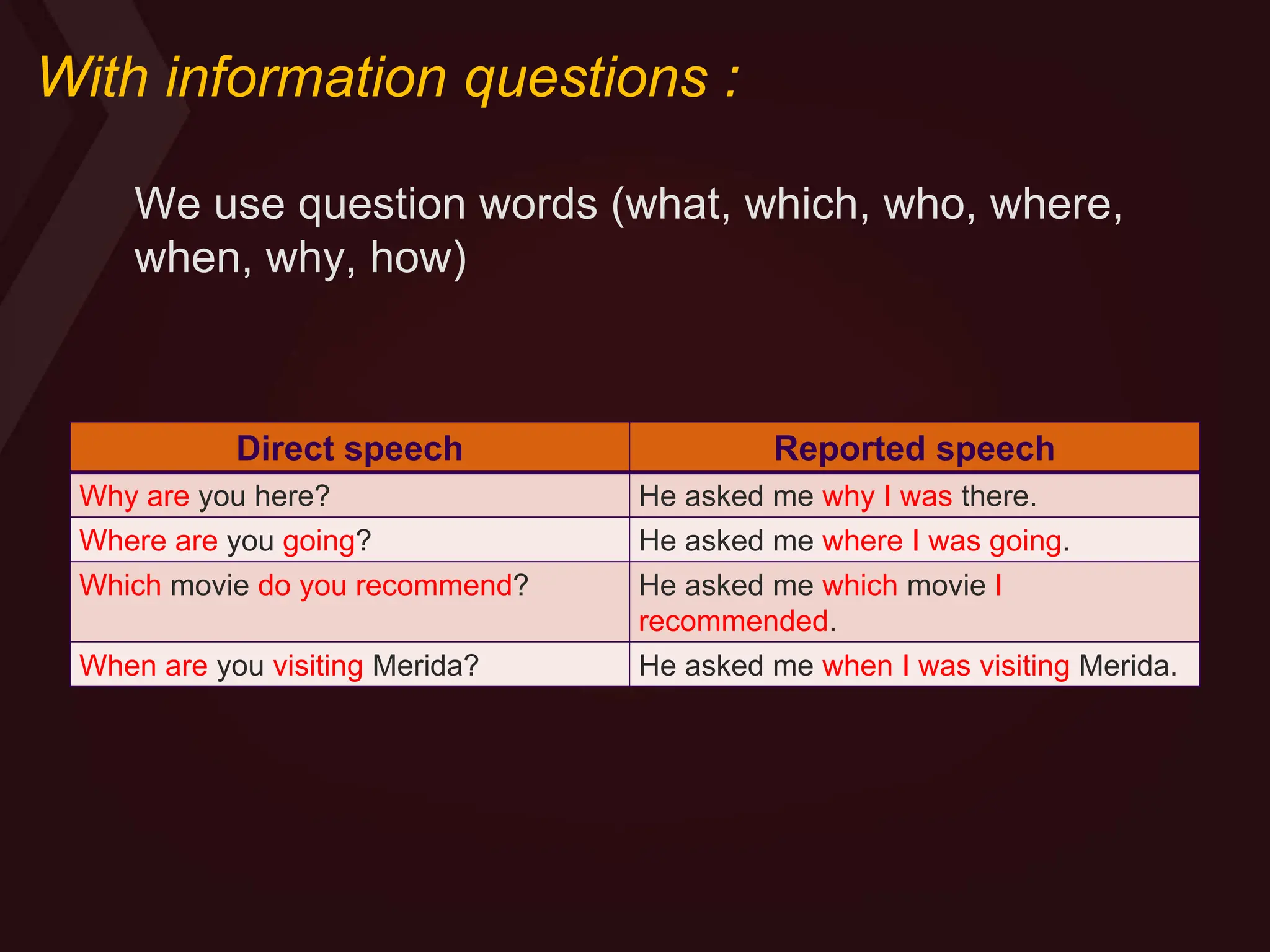
Reported speech is when you tell another person what you or somebody else has said before. There are two forms: direct speech quotes someone verbatim, while reported speech conveys the general idea without quotes. Reported speech often requires changing pronouns, tenses, places, times and demonstratives to reflect the new context. For statements, pronouns may change and the tense may backshift if the reporting verb is in the past tense. Questions are transformed into indirect questions using question words for information questions or "if/whether" for yes/no questions.










![• Referencias
Brook-Hart, G. , (2012) Complete CAE Student’s Book, UK: Cambridge
University Press.
Maxwell, K. (2017). Reported speech 1 – article. [online]
Onestopenglish. Available at:
http://www.onestopenglish.com/grammar/grammar-reference/verbs-and-
tenses/reported-speech-1-article/152841.article [Accessed 29 Aug.
2017].
Schrampfer, B., (2003), Fundamentals of English Grammar, Third
edition, USA: Longman-Pearson Education.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportedspeech-240331154001-c6c6f902/75/Reported_speech-Grammar-presentation-pdf-16-2048.jpg)