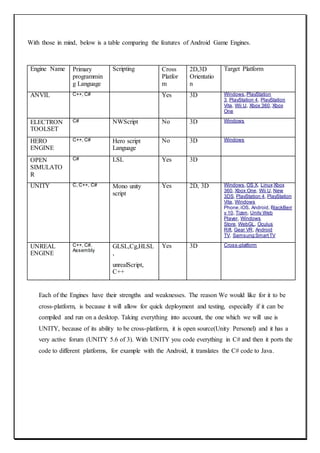
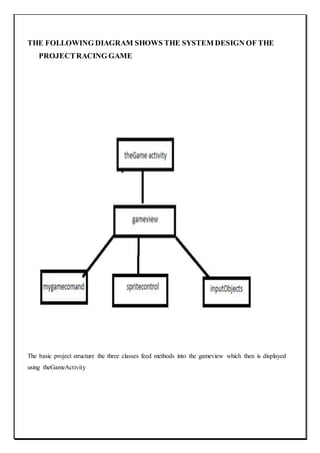
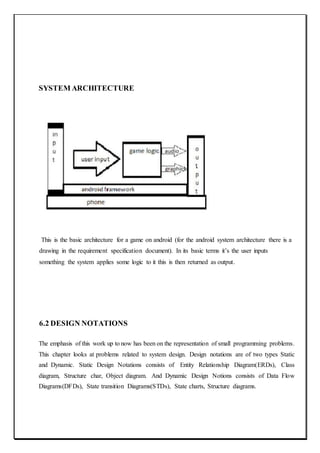
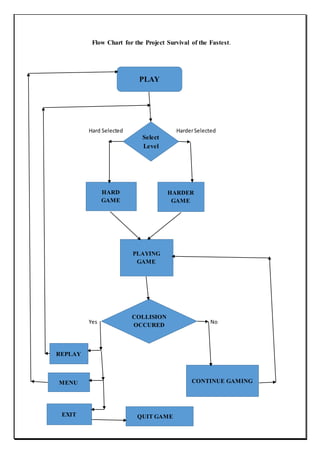
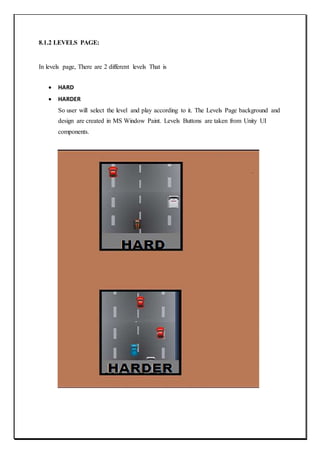
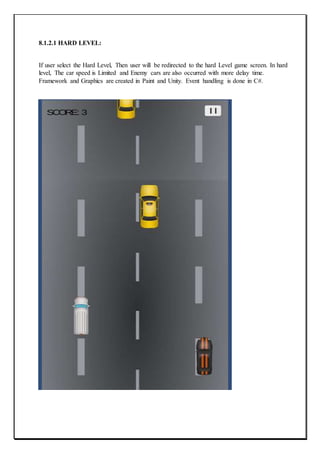
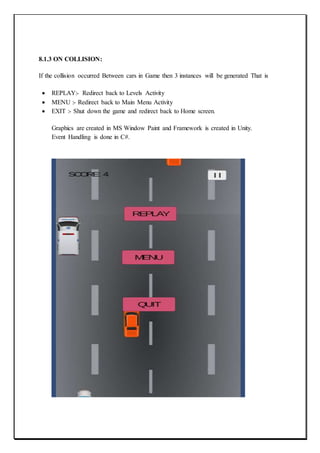
The document describes a capstone project to develop a car racing game called "Survival of the Fastest" using Unity and Android Studio. It was created by three students - Ravijot Singh, Koti Reddy, and Sunil Kumar - under the guidance of their lecturer Mr. Makul Mahajan. The game's objective is to survive as long as possible by avoiding obstacles on the track while getting to high scores quickly. The document outlines the various sections and features that will be included in the project such as introduction, existing applications, framework, design, testing, implementation, project legacy, and source code.


















![Worldwide Developers Conference in 2005, it has since been extended to target more than fifteen
platforms. It is now the default software development kit (SDK) for the Nintendo Wii U.
Unity is notable for its ability to target games to multiple platforms. Within a project, developers
have control over delivery to mobile devices, web browsers, desktops, and consoles. Supported
platforms include BlackBerry 10, Windows Phone 8, Windows, OS X, Linux (mainly
Ubuntu)[citation needed], Android, iOS, Unity Web Player (including Facebook), Adobe Flash,
PlayStation 3, PlayStation 4, PlayStation Vita, Xbox 360, Xbox One, Wii U, and Wii. It includes an
asset server and Nvidia's PhysX physics engine. Unity Web Player is a browser plugin that is
supported in Windows and OS X only. Unity is the default software development kit (SDK) for
Nintendo's Wii U video game console platform, with a free copy included by Nintendo with each
Wii U developer license. Unity Technologies calls this third party provisioning of a free SDK, an
"industry first".
4.2 ANALYSIS
4.2.1 FEASIBILITYSTUDY
A Feasibility study is undertaken to determine the possibility or portability of either improving the
existing system or developing a completely new system.
Feasibility is the measure of how beneficial or practical the development of information system will be
to an organization. The feasibility study involves following criteria.
Wheather the identified user needs may be satisfied using current software and hardware
technologies.
The study will decide if the proposed system will be cost-effective and if it can be developed
given existing budgetary constraints.
The result should inform the decision of whether to go ahead with a more detailed analysis.
There are three methods of feasibility study.
1. Technical feasibility
2. Economic feasibility](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/report-170518203948/85/Report-on-car-racing-game-for-android-20-320.jpg)









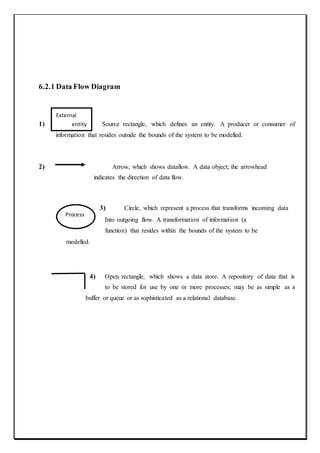
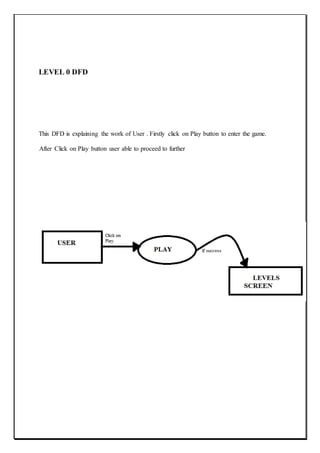
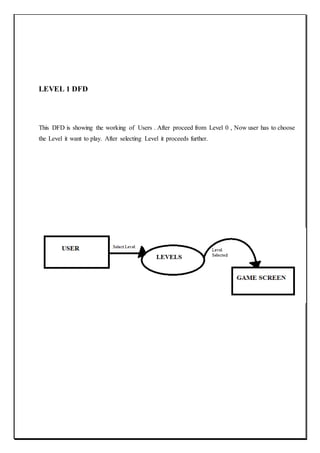
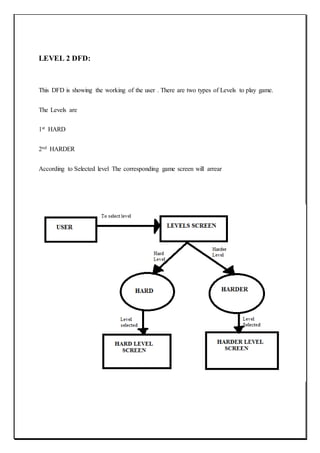











![Section:11
SOURCE CODE
11.1 CODING FOR THE UIMANAGER
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
public class uiManager : MonoBehaviour {
//public Button[] buttons;
public Button[] buttons;
public Text scoreText;
bool gameOver;
int score;
public AudioManager am;
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
gameOver = false;
score = 0;
InvokeRepeating ("scoreUpdate", 7.5f, 0.8f);
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update () {
scoreText.text = "SCORE: " + score;
}
void scoreUpdate(){
if (gameOver == false) {
score += 1;
}
}
public void gameOverActivated(){
gameOver = true;
foreach (Button button in buttons) {
button.gameObject.SetActive(true);
}
}
public void Play()
{
Application.LoadLevel ("Levels");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/report-170518203948/85/Report-on-car-racing-game-for-android-56-320.jpg)




![transform.Translate (new Vector3 (0, -
1, 0) * speed * Time.deltaTime);
}
}
11.5 CODING FOR THE CARSPAWNER
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class CarSpawner : MonoBehaviour {
public GameObject[] cars;
int carNo;
public float maxPos = 2.3f;
float timer;
public float delayTimer;
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
timer = delayTimer;
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update () {
timer -= Time.deltaTime;
if(timer<=0){
Vector3 carPos = new Vector3 (Random.Range (-
2.5f, 2.6f), transform.position.y, transform.position.z);
carNo = Random.Range (0, 7);
Instantiate (cars[carNo], carPos, transform.rotation);
timer = delayTimer;
}
}
}
11.6 CODING FOR THE ENEMYDESTROYER
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class EnemyDestroyer : MonoBehaviour {
// Use this for initialization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/report-170518203948/85/Report-on-car-racing-game-for-android-61-320.jpg)

