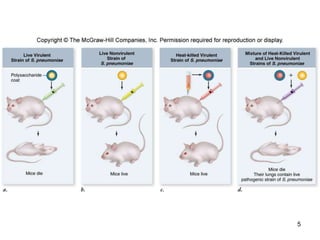
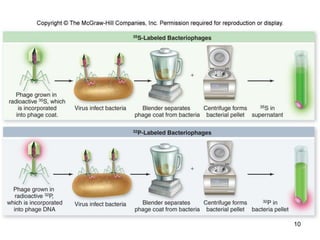
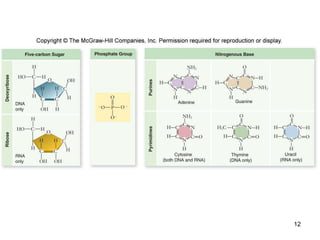
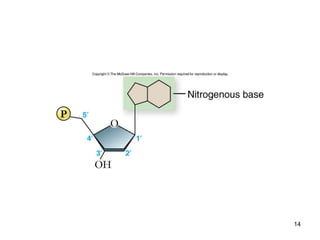
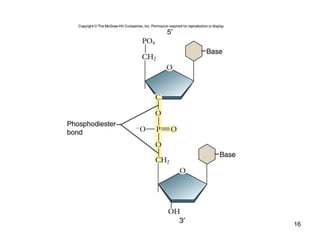
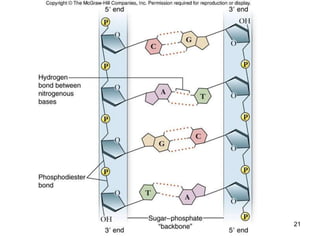
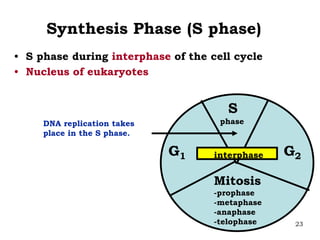
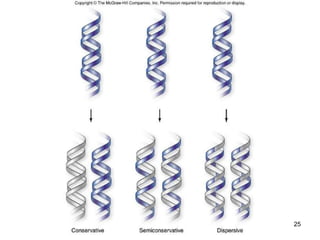
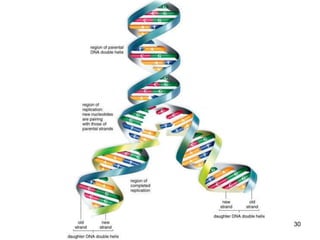
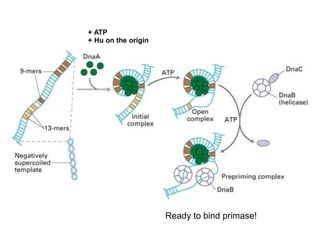
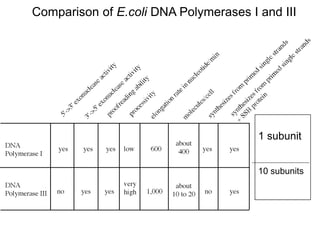
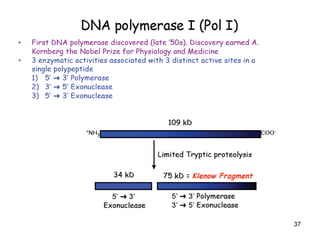
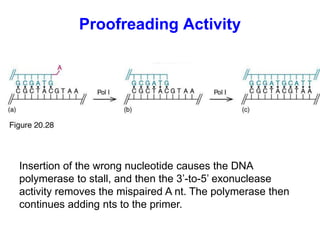
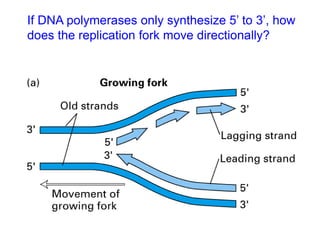
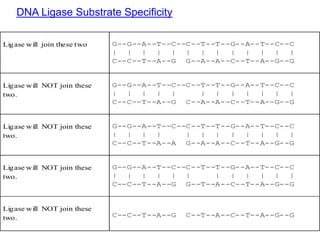
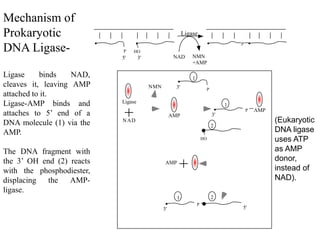
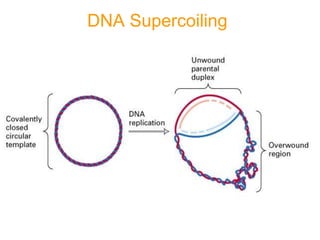
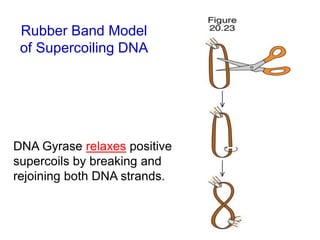
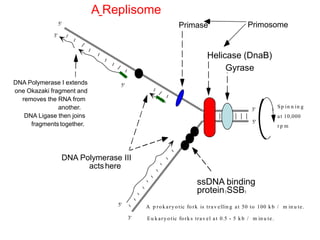
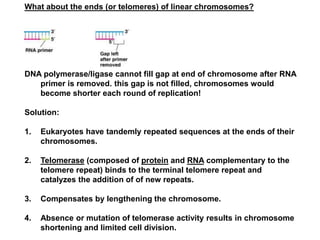
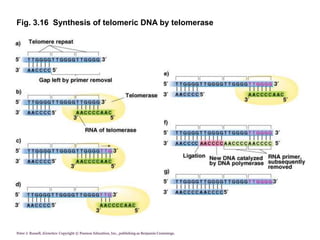
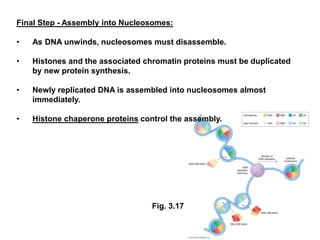
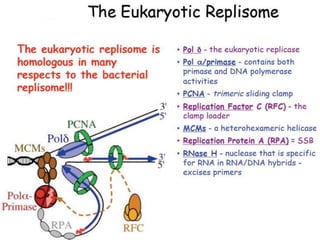
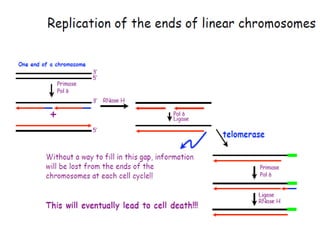
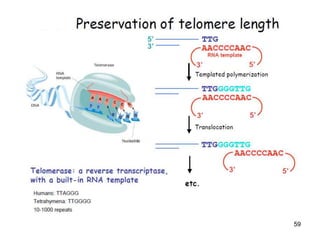
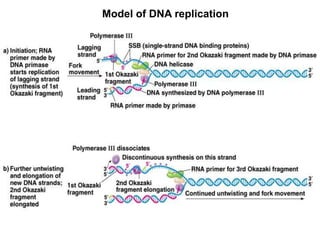
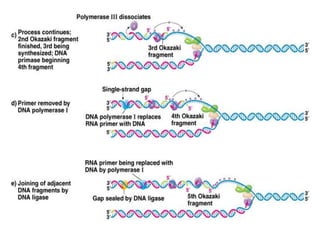
DNA replication is the process where a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division. It is semiconservative, with each parental DNA strand serving as a template for a new daughter strand. Key events include unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicase, addition of nucleotides to the new strands by DNA polymerase, and joining of Okazaki fragments by DNA ligase. Replication occurs bidirectionally from an origin of replication and requires enzymes such as DNA polymerase, helicase, primase, ligase and topoisomerases. Errors can occur but are corrected by proofreading to maintain high-fidelity copying of the genome.