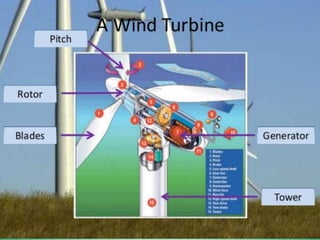
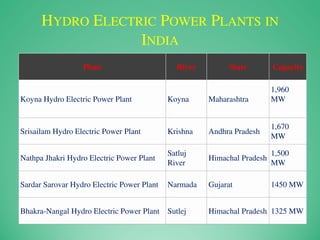
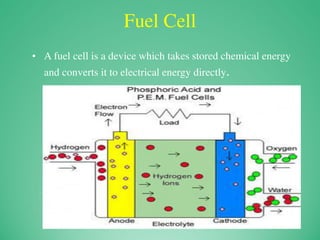
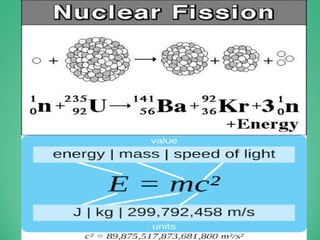
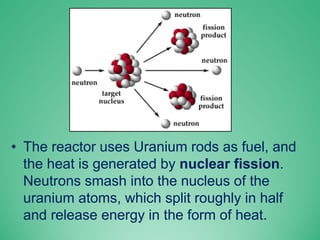
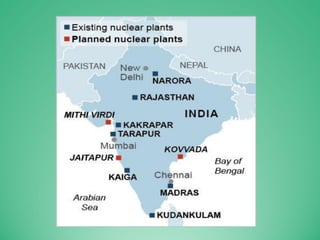
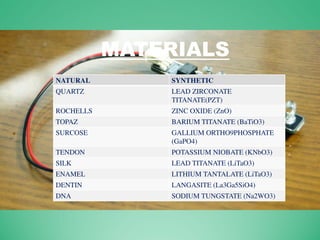
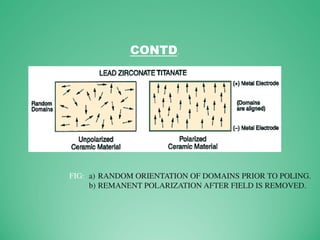
This power point presentation summarizes existing and potential renewable energy sources in India. It was presented by 9 students and guided by Dr. Meenakshi Punia. The presentation discusses various renewable sources including solar power, wind energy, hydroelectricity, tidal power, and biomass energy. For each source, it provides background information on how the technology works, existing and planned projects in India, as well as advantages and disadvantages. The largest sections focus on solar power and wind energy, outlining India's growth in these sectors in recent years.