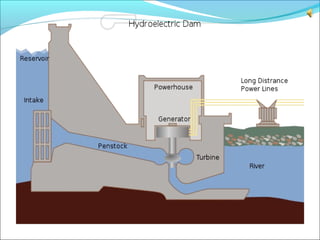
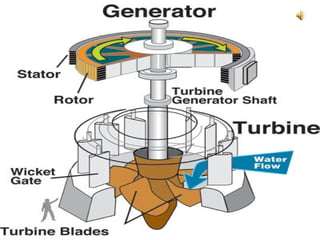
Hydroelectricity is a form of renewable energy generated through hydropower by harnessing the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used renewable energy source, providing approximately 20% of worldwide electricity in 2006. Hydroelectric plants have lower carbon dioxide emissions than fossil fuel plants once constructed and produce no direct waste. Key components of hydroelectric systems include dams to store water, penstocks to transport water under pressure, turbines converted by the water's kinetic energy, generators to produce electricity, and transformers to adjust voltage for transmission to electric grids.