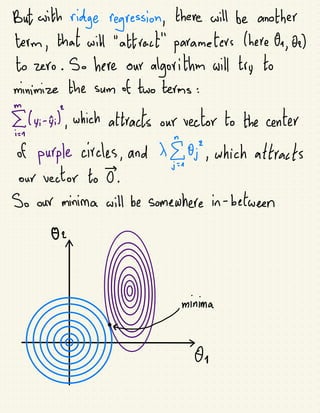
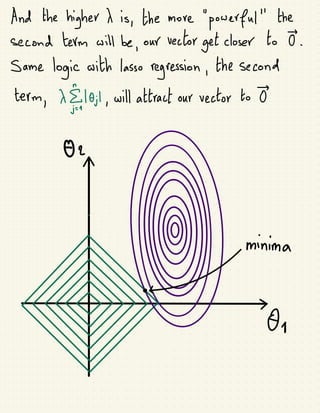
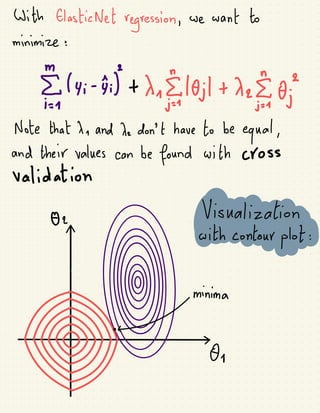
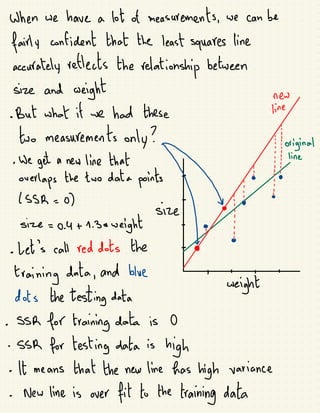
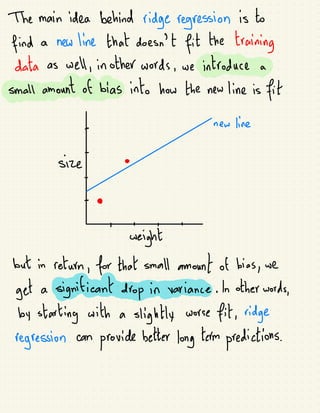
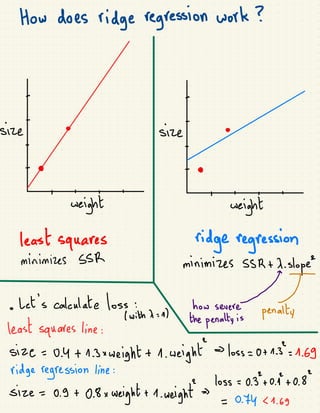
The document discusses various regularization techniques in machine learning, including ridge regression, lasso regression, and elastic net regression, which are used to minimize overfitting by introducing bias and reducing variance. Ridge regression improves predictions by penalizing the sum of squared residuals along with a term based on the slope, while lasso regression can completely eliminate irrelevant variables by shrinking their coefficients to zero. Elastic net regression combines the strengths of both ridge and lasso, allowing for the selection of the best regularization method based on the characteristics of the dataset.






![Minimizing RSS +
18
8
(y -
x0)"(y -
x8) +
x0
y*y -
28xy +
8xx6 +
x8 8
because (X8)"= 8x*
&y-28x4 +
0x6 +
x0%
=
-
2X*y +
2xx8 +
8x8
68
set it
equal to 0, solve for 8
0 =
- 2xxy +
exx8 +
ex8
0 =
- x*y +
xx +
x8
x*y =
x
+
x6 +
x8
x*y =
(xx +
xI)8
(xx +
x])x*y =
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regularisationinml-240531170145-fcc981ac/85/Regularisation-in-Machine-Learning-notebook-10-320.jpg)