This document discusses refinements in the art of radio surgical treatment of cranial lesions. Key points include:
1) Improvements in neuroimaging, neuroanatomy knowledge, and radiation therapy delivery systems have enhanced radio surgical treatments.
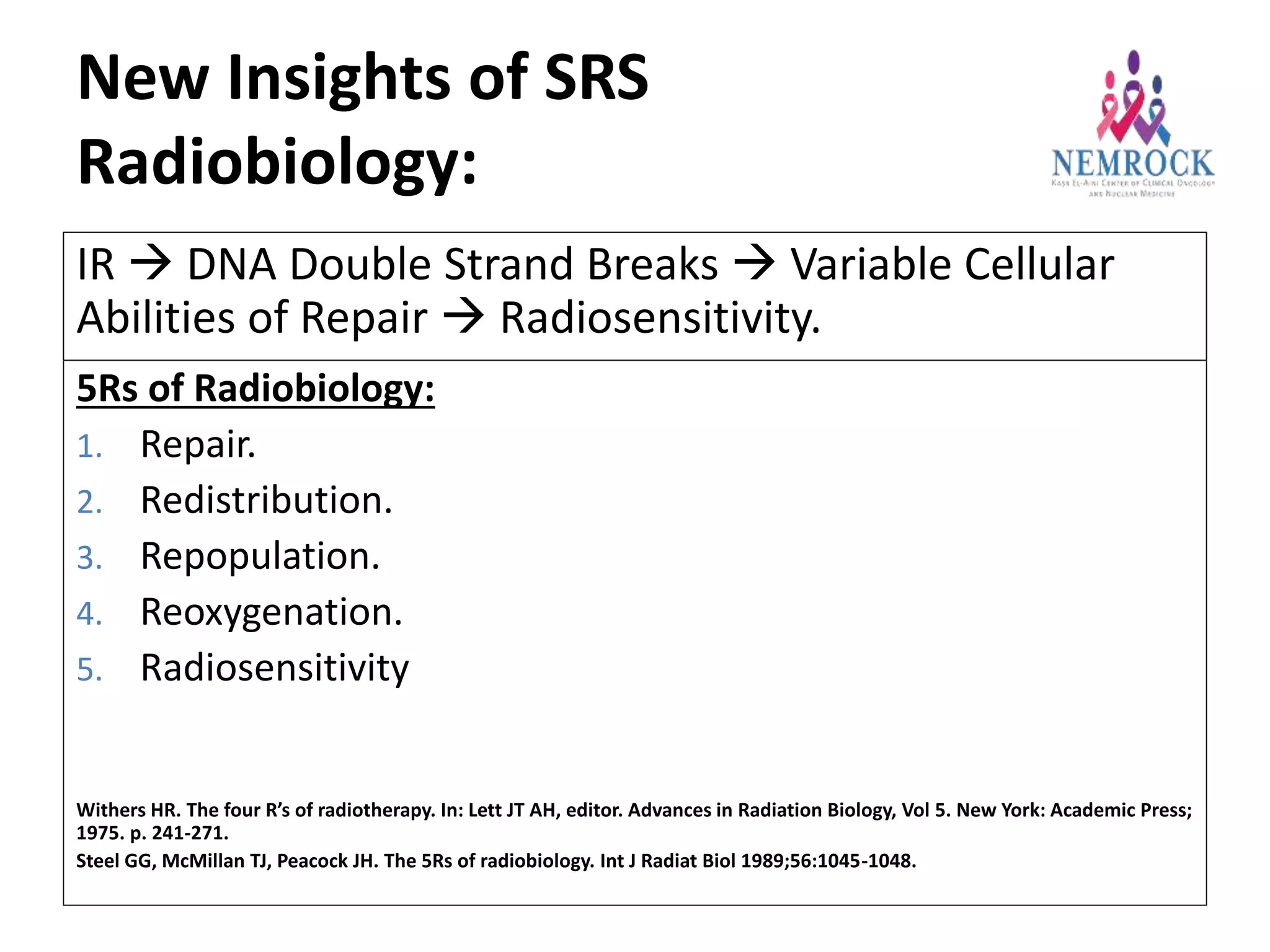
2) A better understanding of radiobiology, such as the 5 R's of radiobiology and effects of single high doses, has provided new insights.
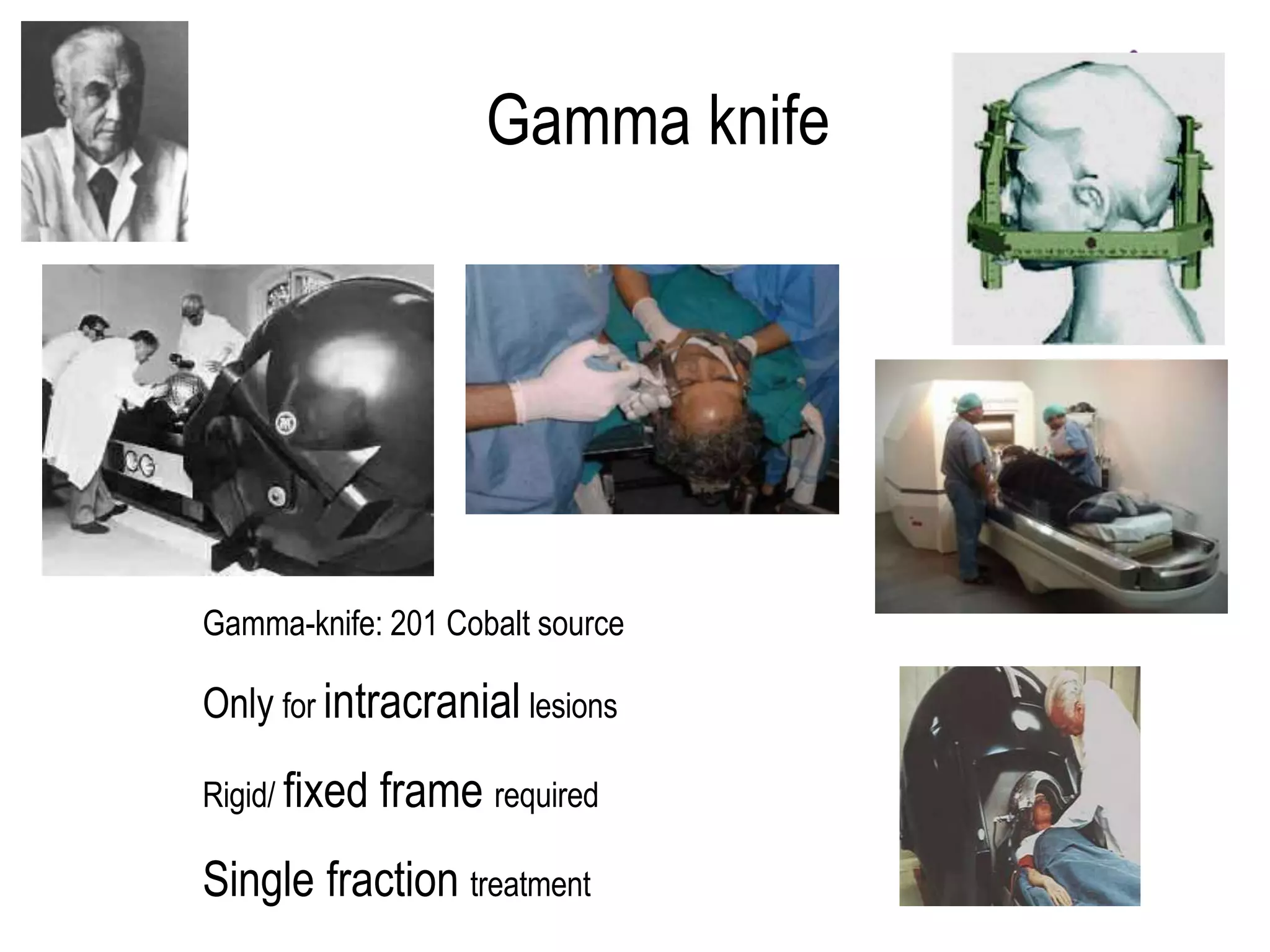
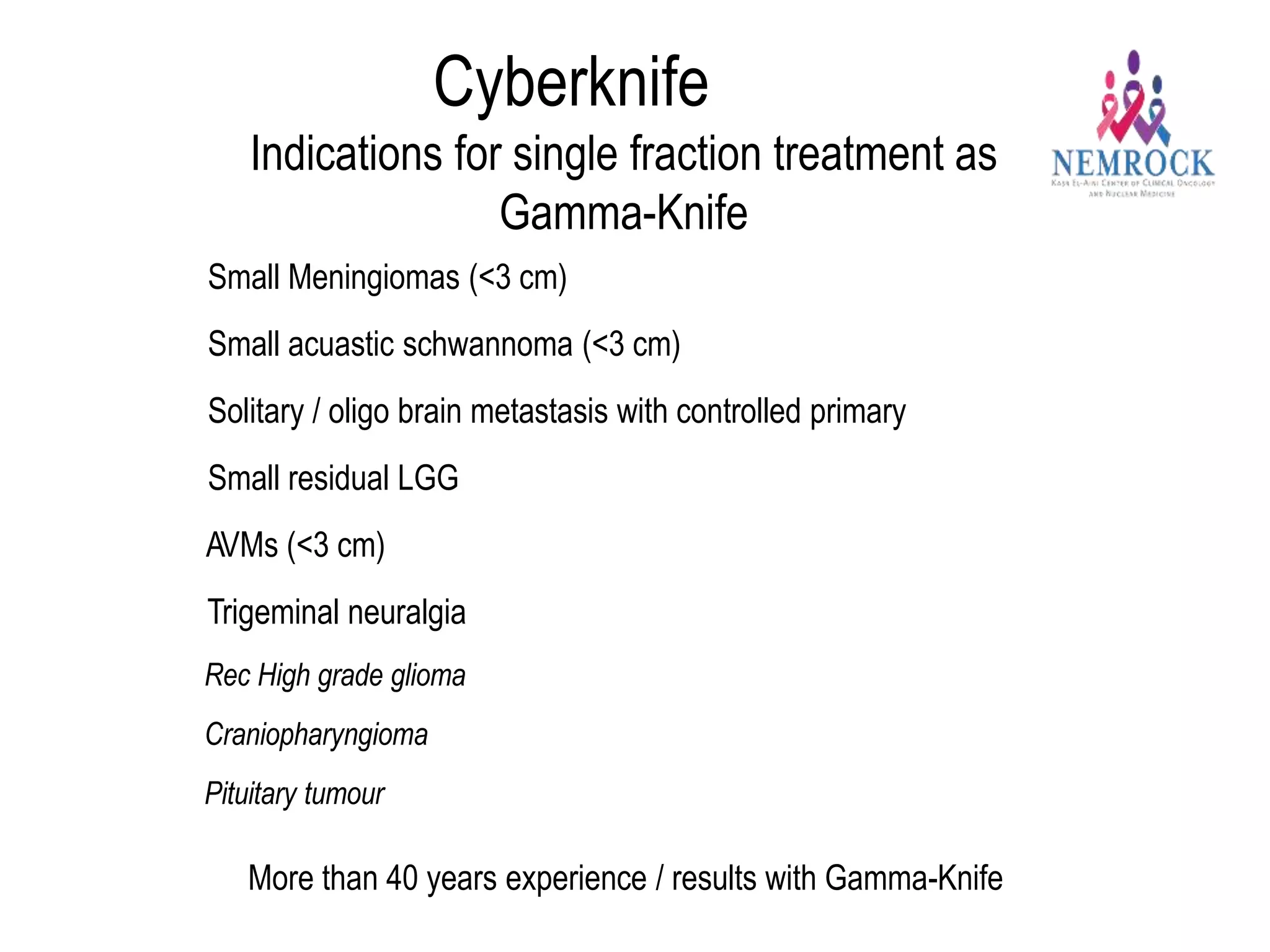
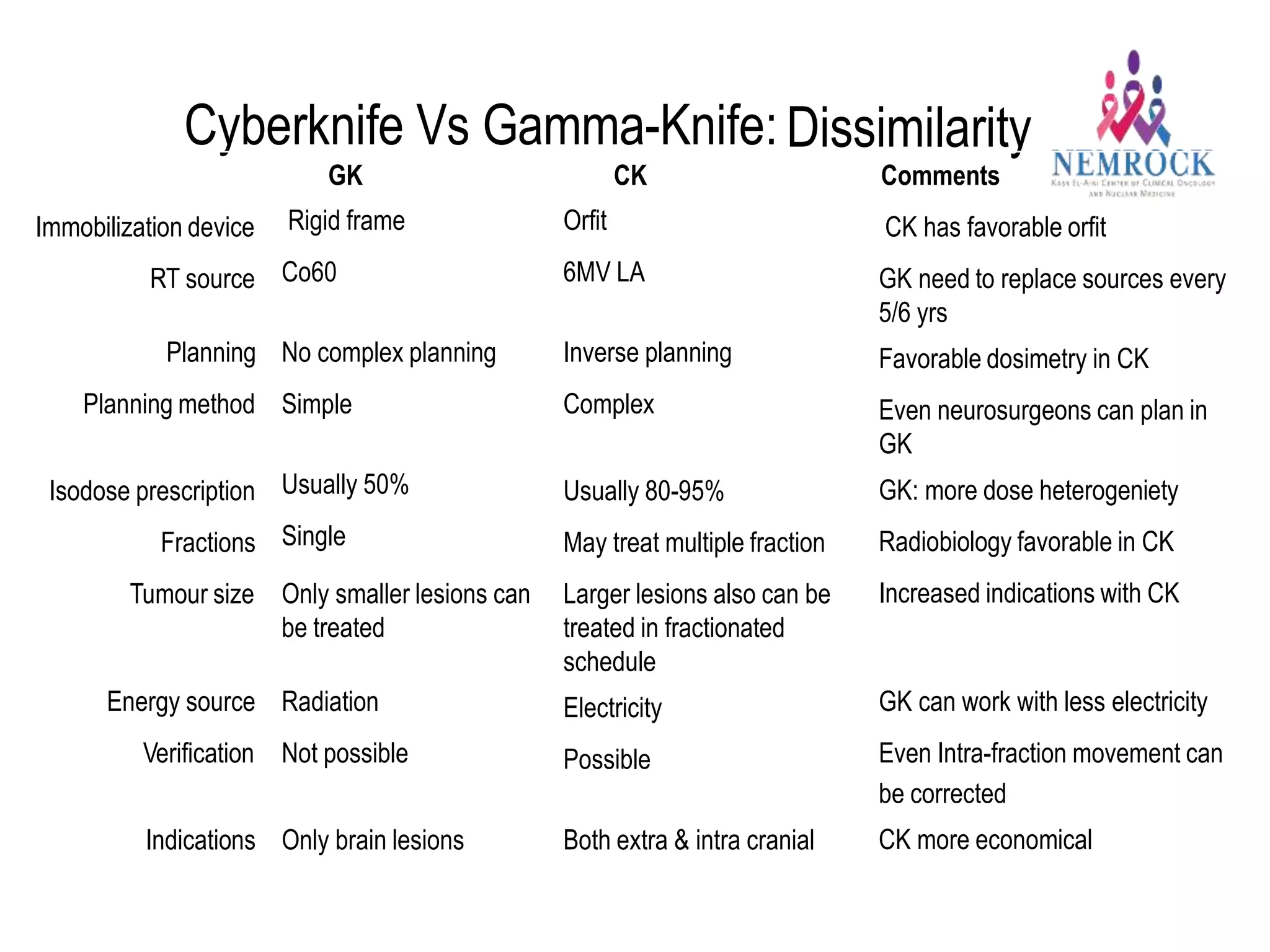
3) Technologies like Gamma Knife, CyberKnife, and linear accelerator-based systems have expanded indications for radio surgery to include larger and extracranial lesions through fractionation.