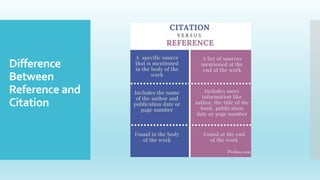
This document discusses the differences between citations and references in academic writing. It explains that referencing allows writers to acknowledge the work of others, citations provide credit to original authors, and references are included in a standardized format. There are four main referencing styles - MLA, APA, Harvard, and MHRA. Citations provide details needed for readers to locate sources in a reference list and come in different formats like parenthetical, numerical, or footnote citations. The document outlines rules for citations, such as including author name, title, and date, and ensuring consistency between in-text citations and reference list entries.