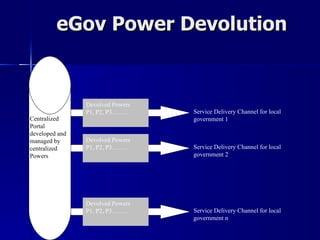
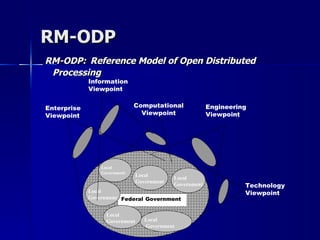
The document presents a reference model for devolution in e-governance, focusing on centralized and decentralized approaches and their characteristics. It outlines a proposed framework addressing issues like governance, service delivery, and data integration, emphasizing the necessity of coordination between various levels of government. The model categorizes devolved powers and identifies dependencies, constraints, and prerequisites necessary for effective implementation.