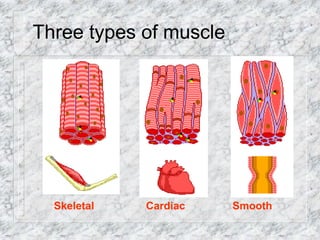
- More than 50% of the human body is composed of muscle. There are three main types of muscle: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
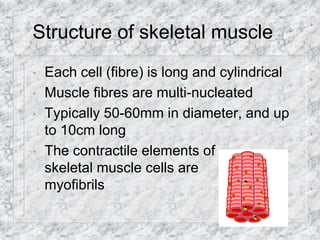
- Skeletal muscle is voluntary, striated muscle found attached to bones that facilitates movement. It has long, multi-nucleated cylindrical fibers.
- Cardiac muscle is involuntary, striated muscle found only in the heart. It has branched fibers connected by intercalated discs that contract in unison.
- Smooth muscle is involuntary, non-striated muscle that lines internal organs. It has spindle-shaped, single-nucleated fibers that facilitate movements like peristalsis.