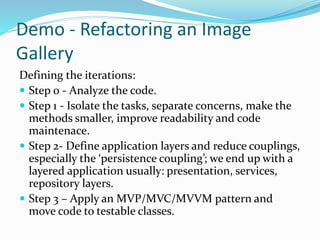
The document discusses the process and best practices for refactoring code, emphasizing the importance of clean-up, readability, and maintainability. It outlines a structured refactoring pipeline that includes analyzing legacy code, setting objectives, and iterating through tasks to improve code organization. The document also provides specific steps for refactoring an image gallery and encourages rigorous testing throughout the process.


![MVP Team System
Blog: http://www.nablasoft.com/alkampfer [Eng]
http://blogs.ugidotnet.org/rgm [Ita]
Email: alkampfer@nablasoft.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoringwithresharper-140828050847-phpapp01/85/Refactoring-ASP-NET-and-beyond-3-320.jpg)