Redis is an open source, advanced key-value store that can be used as a data structure server. It supports various data structures like strings, hashes, lists, sets, and sorted sets. Redis has features like speed, simplicity, reliability and versatility. It can be installed by downloading from the Redis website. The Redis server listens on port 6379 by default. Popular programming languages have client libraries available to connect to Redis. Redis supports different data structures that can be used for applications like caching, sessions, messaging, and more. Data sets in Redis are stored in memory for fast access but can also be persisted to disk for durability.



















![Set Relationship
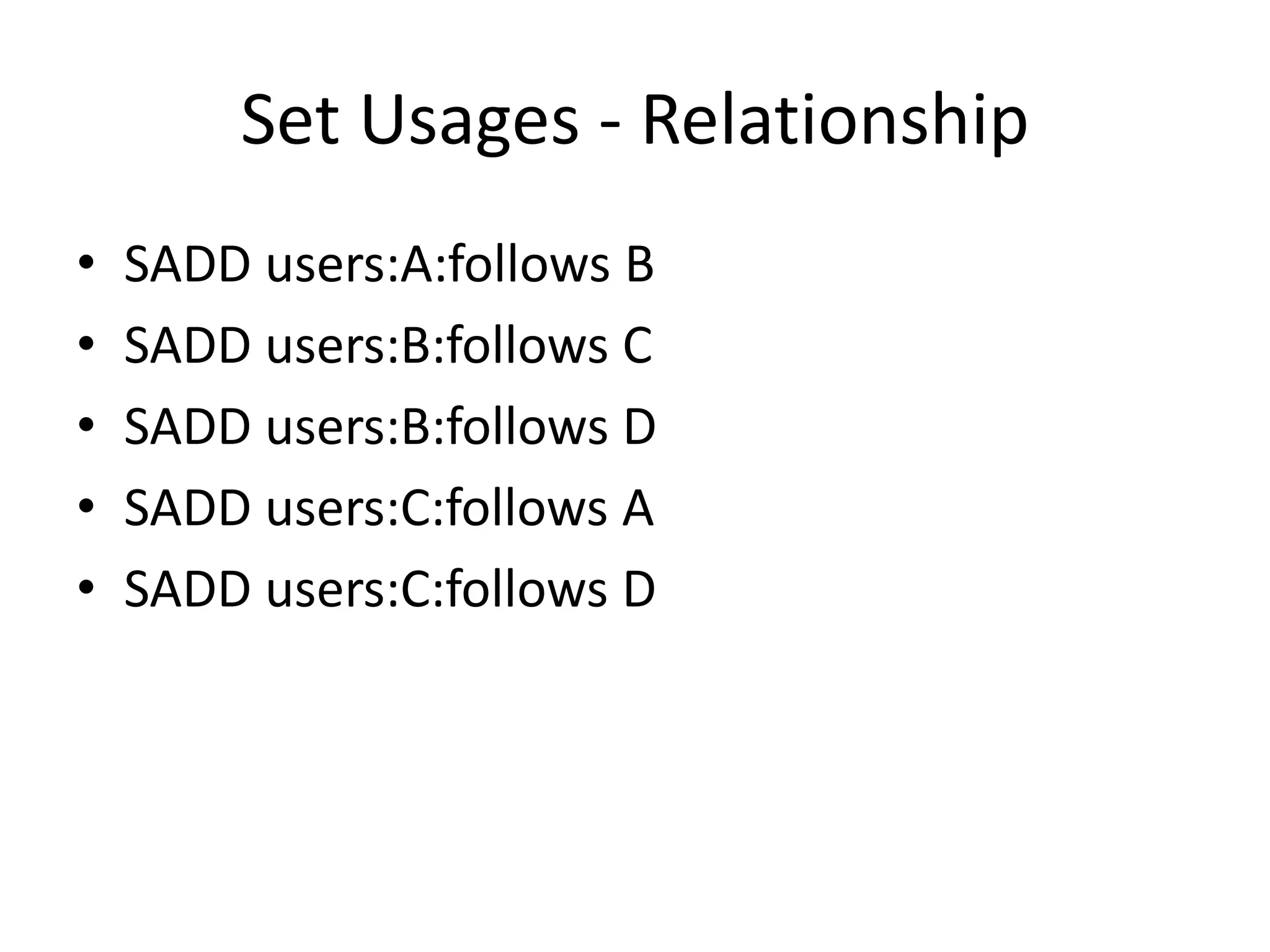
• Joint network of A & B
SUNION users:A:follows users:B:follows
“C”,”D”,”B”
• Common for A & B
SINTER users:B:follows users:C:follows
[]
• Unique to B compared to C
“C”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/88373ea9-ba77-4c04-9517-87eeae3f8e9f-150327120057-conversion-gate01/75/REDIS327-21-2048.jpg)