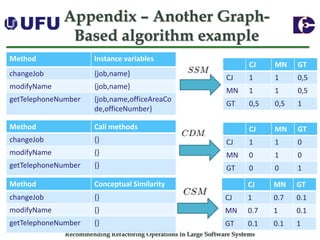
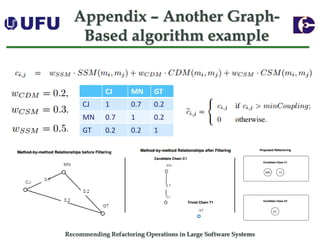
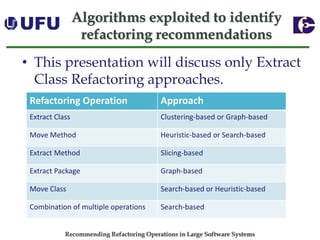
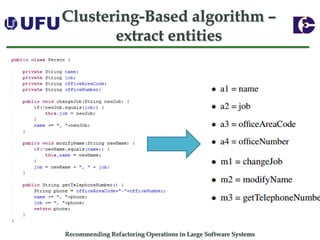
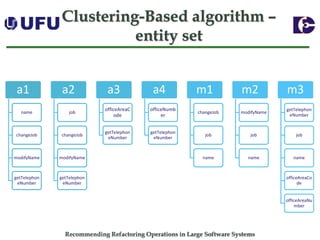
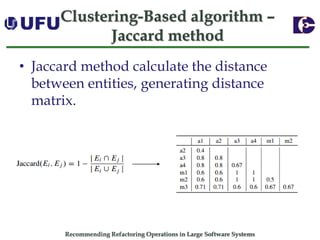
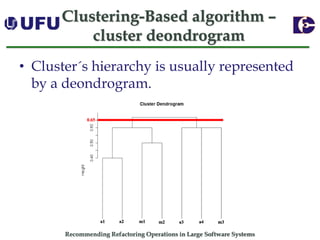
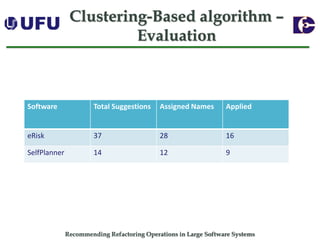
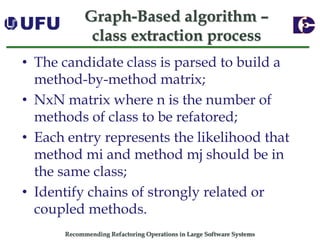
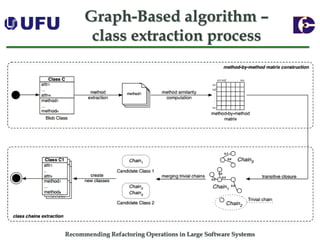
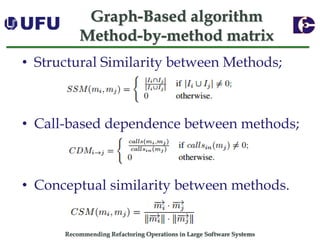
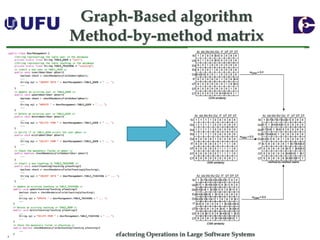
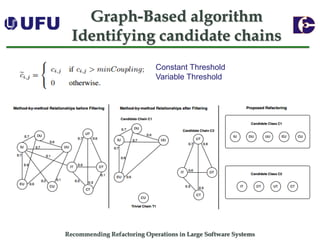
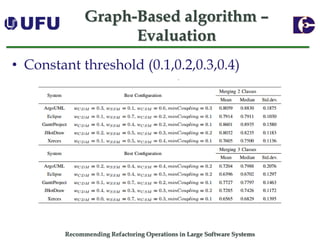
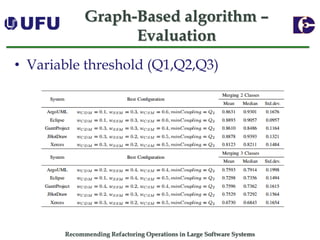
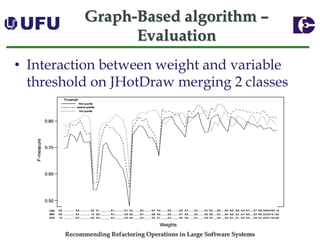
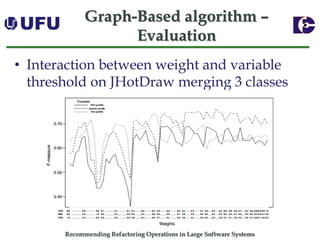
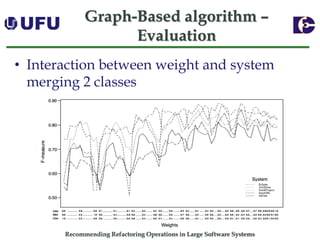
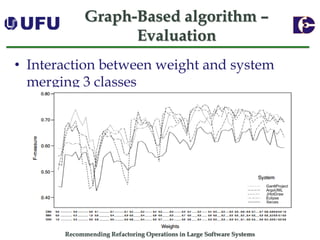
The document discusses algorithms for recommending refactoring operations in large software systems. It describes two main algorithms - a clustering-based algorithm and a graph-based algorithm. The clustering-based algorithm identifies groups of similar methods and entities that could be extracted into separate classes. The graph-based algorithm builds a matrix of relationships between methods and identifies strongly related chains of methods that could form candidate classes. Both algorithms were evaluated on open source systems and shown to effectively recommend extract class refactoring opportunities.





![Recommending Refactoring Operations in Large Software SystemsReferences
•[1] Robillard, Martin P.:, Maalej, Wallid.: Recommendation Systems in Software Engineering. Springer, 2014;
•[2] Fokaefs, M., Tsantalis, N., Chatzigeorgiou, A., Sander, J.: Decomposing object-oriented class modules using an agglomerative clustering technique. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance, (2009);
•[3] Fowler, M.: Refactoring: improving the design of existing code. Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1999;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendingrefactoringoperationsinlargesoftwaresystems-140915073755-phpapp02/85/Recommending-refactoring-operations-in-large-software-systems-27-320.jpg)
![Recommending Refactoring Operations in Large Software SystemsReferences
•[4] Fokaefs, M., Tsantalis, N., Stroulia, E., Chatzigeorgiou, A.: Identification and application of extract class refactoringsin object-oriented systems. J. Syst. Software 85(10), 2012;
•[5] Bavota, G., De Lucia, A., Marcus, A., Oliveto, R.: Automating extract class refactoring: a Novel Approach and its Evaluation, 2011;
•[6] Bavota, G., De Lucia, A., Marcus, A., Oliveto, R.: In Medio Stat Virtus: Extract Class Refactoring through Nash Equilibria, 2011.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendingrefactoringoperationsinlargesoftwaresystems-140915073755-phpapp02/85/Recommending-refactoring-operations-in-large-software-systems-28-320.jpg)