1. The document describes 5 main types of chemical reactions: synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion.
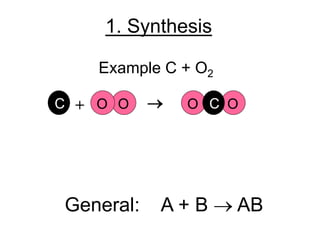
2. Synthesis reactions involve combining two or more reactants to form a single new product. Decomposition reactions involve breaking down a single reactant into simpler products.
3. Single displacement reactions involve one element replacing another in a compound. Double displacement reactions involve the exchange of ions between two reactants to form two new products.
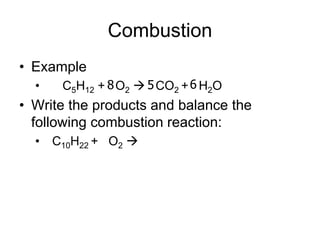
4. Combustion reactions involve hydrocarbons reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.